mechanical behavior
how a material (or structure) responds to loads
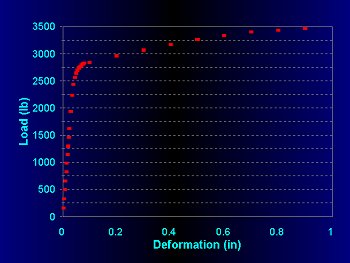
Load-Deformation Diagram
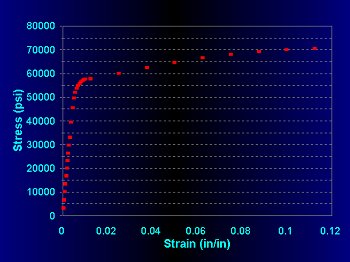
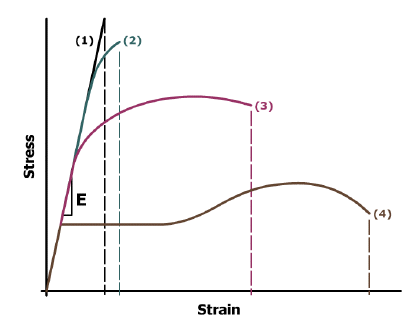
Stress-Strain Diagram
stress-strain diagrams
-
modulus of elasticity, E = slope of intial linear part of the stress-strain curve
-
proportional limit stress, σpl = stress value at which the stress-strain curve goes nonlinear
-
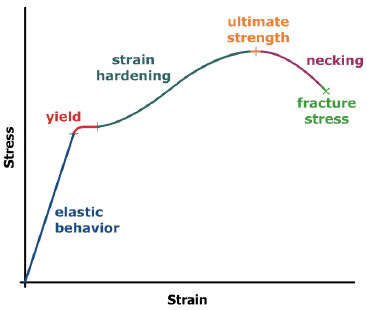
yield point stress, σy = stress value at which the stress-strain curve goes horizontal (for many steels)
-
0.2%-offset yield stress, σ0.2% yp = the stress value at which a line drawn with slope E starting at 0.002 strain intersects the stress-strain curve
-
ultimate tensile stress, σult = largest stress on the stress-strain curve (top of the curve)
-
engineering fracture stress = fracture load / original area
-
true fracture stress = fracture load / fracture area
-
energy at yield = area under the elastic portion of the load-deformation curve
-
energy at break = area under the entire load-deformation curve
-
modulus of resilience, Ur = area under the elastic portion of the stress-strain curve = σpl2 / 2E = the amount of energy (or work) stored per unit volume at the elastic limit
-
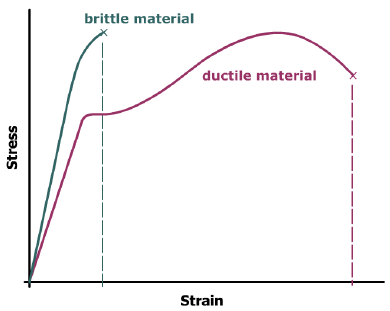
modulus of toughness, Ut = area under the entire stress-strain curve = the amount of energy absorbed per unit volume at fracture -- a measure of the material ductility
-
percent elongation = (Lf - Lo) / Lo x 100%
-
Percent Elongation of 2" Gage Length = ΔL2 / 2" x 100%
- Percent Elongation of 8" Gage Length = ΔL8 / 8" x 100%
-
-
percent reduction in area = (Af - Ao) / Ao x 100%