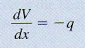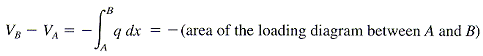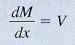In other words...
- change in shear = negative of area under distributed-loading curve
- change in moment = area under shear-force diagram
The shear force changes abruptly at the point of application of a concentrated load but not a couple.
- If a concentrated force acts upward on the beam, the shear will jump upward by the amount of the force.
- If a concentrated force acts downward on the beam, the shear will jump downward by the amount of the force.
- If a clockwise couple moment acts on the beam, the shear will not be affected, however, the moment diagram will jump upward by the amount of the moment.
- If a counterclockwise couple moment acts on the beam, the shear will not be affected, however, the moment diagram will jump downward by the amount of the moment.
Points of zero shear represent points of maximum or minimum moment since dM/dx = 0.