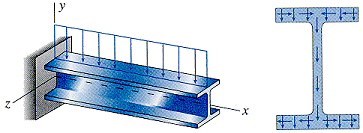
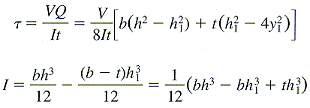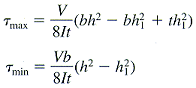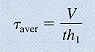Shear stress in wide-flange beams is more complicated than rectangular beams.
- Shear stresses in the flanges act both vertically and horizontally, which we will not study this semester.
- Shear stresses in the web act only vertically and can be determined as in rectangular beams.
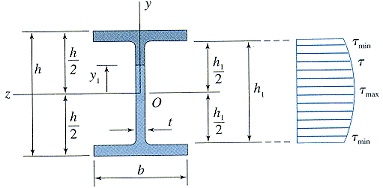
assumptions
- shear stresses act parallel to the y axis
- shear stresses are uniformly distributed across the thickness of the web
- the effects of the small fillets at the juncture of the web and flange can be ignored
shear stresses in the web
This τmax will be the largest shear stress anywhere in the beam.
shear force in the web
The vertical shear force carried by the web alone can be determined by multiplying the area of the shear-stress diagram by the thickness of the web.
Typically, the web carries 90 to 98% of the total shear force V acting on the cross section, while the the flanges carry the remainder.
A quick way to approximate the shear stress in the web is to divide the shear force by the web area. This assumes the web carries all of the shear load.
This value is generally within 10% of τmax calculated above.