|
Enter two columns of random numbers with headers in Excel.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
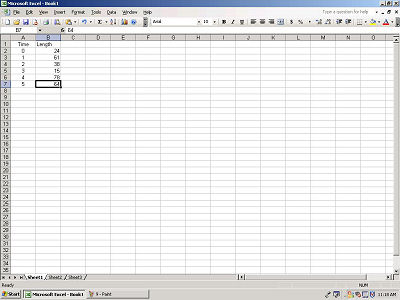
Now select an empty cell off to the side of your first two columns.
Type in "=(" to begin your formula.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
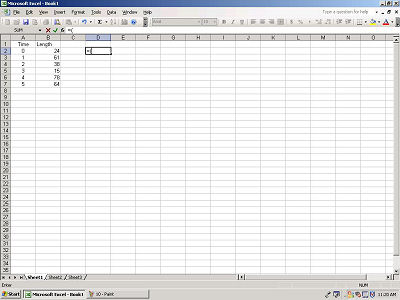
To denote a certain cell's data as a variable, use its column letter and
row number. Enter this information after your "=(".
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
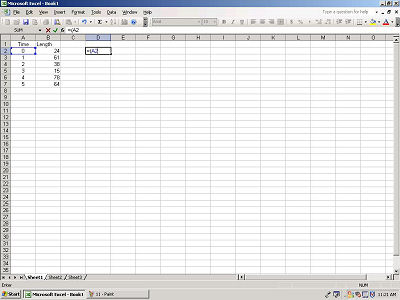
Now select an operation to perform. To add, use a "+",
to subtract, use a "-", to multiply, use a "*", and
to divide, use a "/". We will multiply the first and
second columns of row 2. To finish your formula, put in a
")".
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
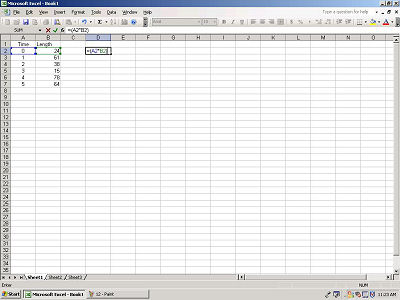
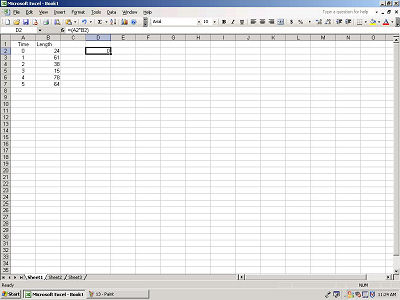
To calculate the value of this cell, hit ENTER.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
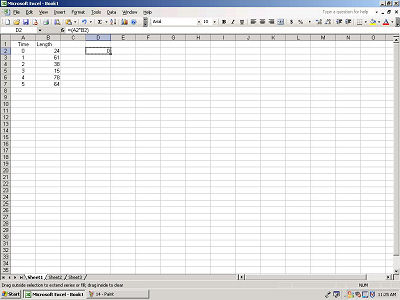
Excel allows users to spread formulas to different cells. To do
this, click on the lower right corner of the cell that contains your
formula.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
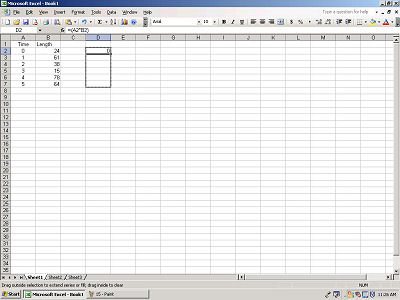
Next, drag this light gray box to the last row with data.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
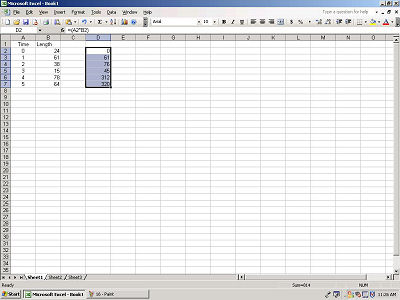
Let go of the left mouse button and your values should appear.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
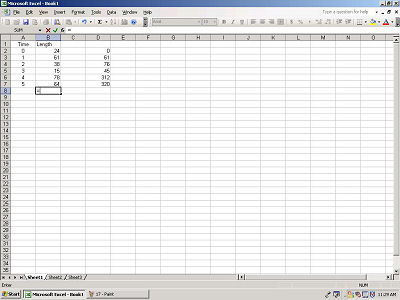
Now let's total a function. Select a cell directly beneath your
second column. Enter an "=".
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
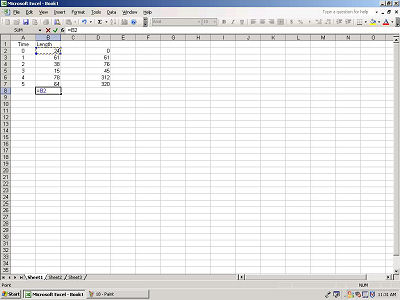
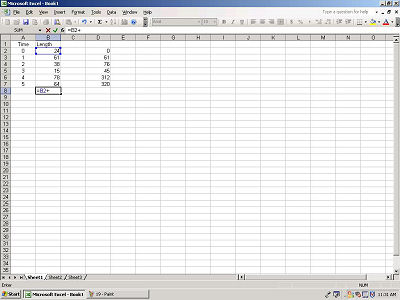
Select each cell in the column and hit the "+" between each
selection.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
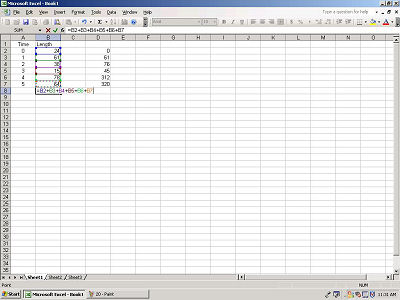
Now hit ENTER and your column has been totaled.
Remember, Excel uses standard orders of operation for mathematics, so
use parenthesis as needed.
|
|
 |