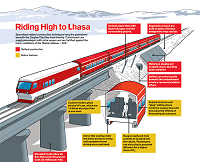
| It is the largest construction project built on
permafrost
since the Trans-Alaska Pipeline was completed in 1977.
In areas where elevated track didnít make sense or
proved too expensive, sections of the railway are lined with
vertical pipes that circulate liquid nitrogen. In other
places, hollow concrete pipes beneath the tracks create a
reverse-insulating effect. Metal sun shades were also placed
in a few south-facing locations to reduce warming from the
sun. Another
experimental cooling strategy involved building track
foundations with stones of various sizes. When piled
together, they create pockets that retain cool air.
|