| Material | Density (Mg/m3) |
Modulus (GPa) |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
| Wood | 0.1-1 | 0.2-20 | 25-100 |
| Polymer | 1-2 | 0.01-10 | 5-100 |
| Ceramic | 1-5 | 10-1000 | 1-800 |
| Metal | 2-10 | 50-200 | 50-2000 |
| Material | Specific Strength (x105 psi) |
Specific Modulus (x107 psi) |
| Clear wood | 7 | 9.5 |
| Aluminum | 5 | 10.5 |
| 1020 steel | 2 | 10.5 |
| Copper | 1.5 | 5.5 |
| Concrete | 0.6 | 3.5 |
E varies a lot between wood types and between individual samples within the same type, due to variations in grain pattern and knot size and quantity.
| Wood | Density (for 12% water) (g/cm3) |
Modulus of Elasticity (psi) |
| Cedar | 0.32 | 1,100,000 |
| Pine | 0.35 | 1,200,000 |
| Fir | 0.48 | 2,000,000 |
| Maple | 0.48 | 1,500,000 |
| Birch | 0.62 | 2,000,000 |
| Oak | 0.68 | 1,800,000 |
Strengths also vary greatly. Note the anisotropic behavior of the following wood types classified by grain pattern and load type.
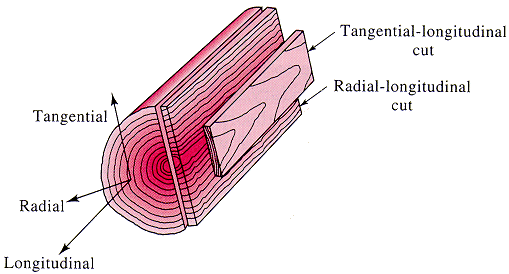
| Wood | Tensile Strength Longitudinal (psi) |
Tensile Strength Radial (psi) |
Compressive Strength Longitudinal (psi) |
Compressive Strength Radial (psi) |
 from The Science and Technology of Civil Engineering Materials, J.F. Young, et al., Prentice Hall, 1998. |
|
| Beech | 12,500 | 1,010 | 7,300 | 1,010 | ||
| Elm | 17,500 | 660 | 5,520 | 690 | ||
| Maple | 15,700 | 1,100 | 7,830 | 1,470 | ||
| Oak | 11,300 | 940 | 6,200 | 810 | ||
| Cedar | 6,600 | 320 | 6,020 | 920 | ||
| Fir | 11,300 | 390 | 5,460 | 610 | ||
| Pine | 10,600 | 310 | 4,800 | 440 | ||
| Spruce | 8,600 | 370 | 5,610 | 580 |
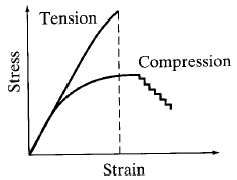
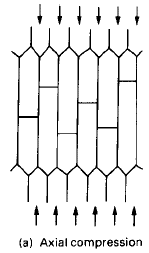 |
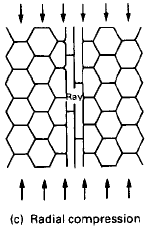 |
 |
from Engineering Materials 2, M.F. Ashby, R.H. Jones, Pergamon Press, 1986, p. 260. |