General Principles
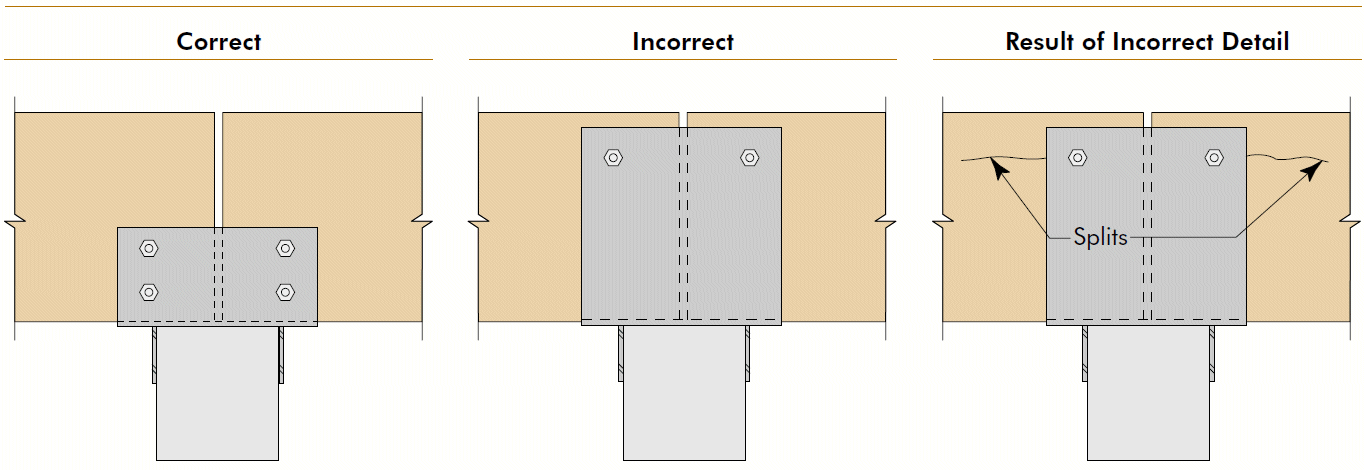
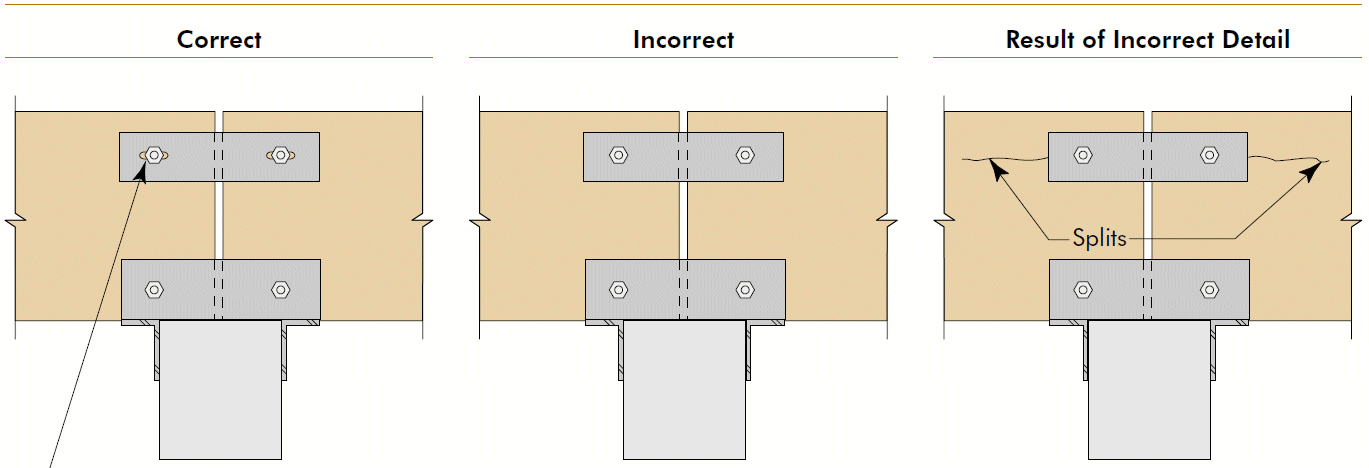
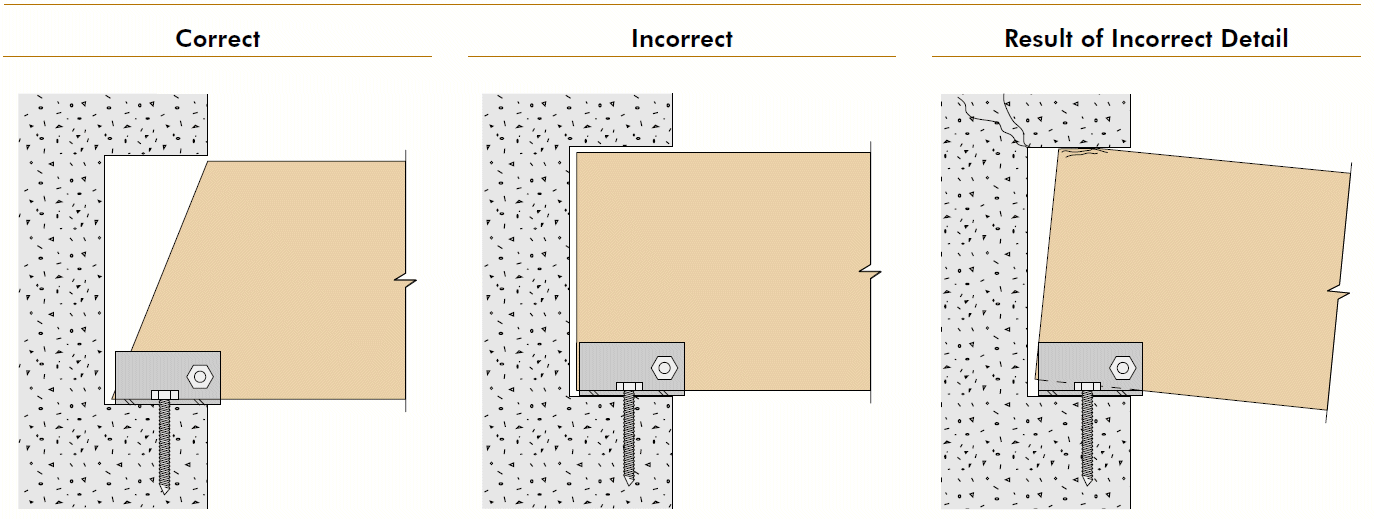
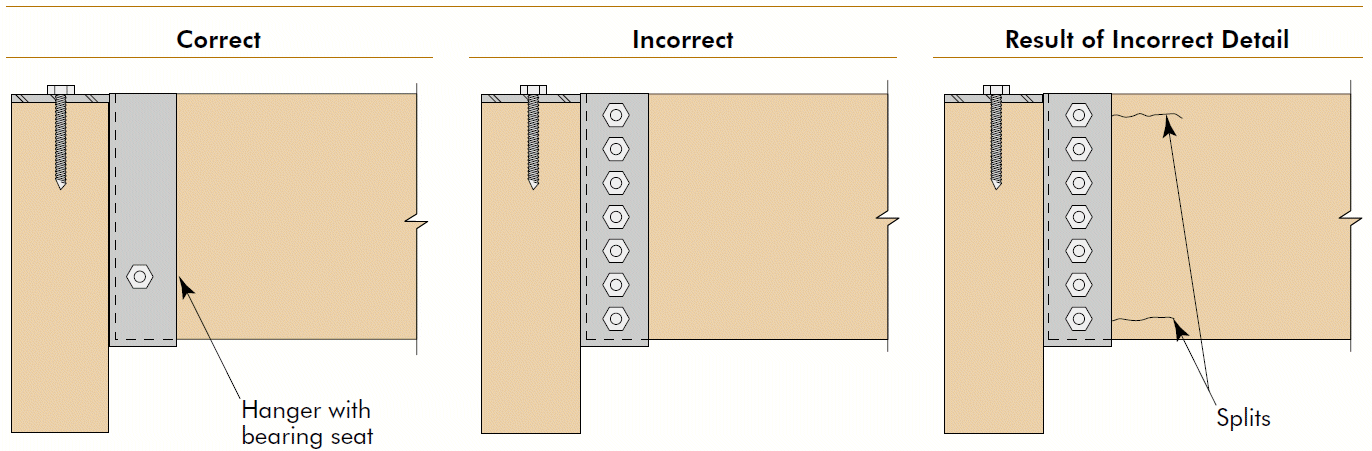
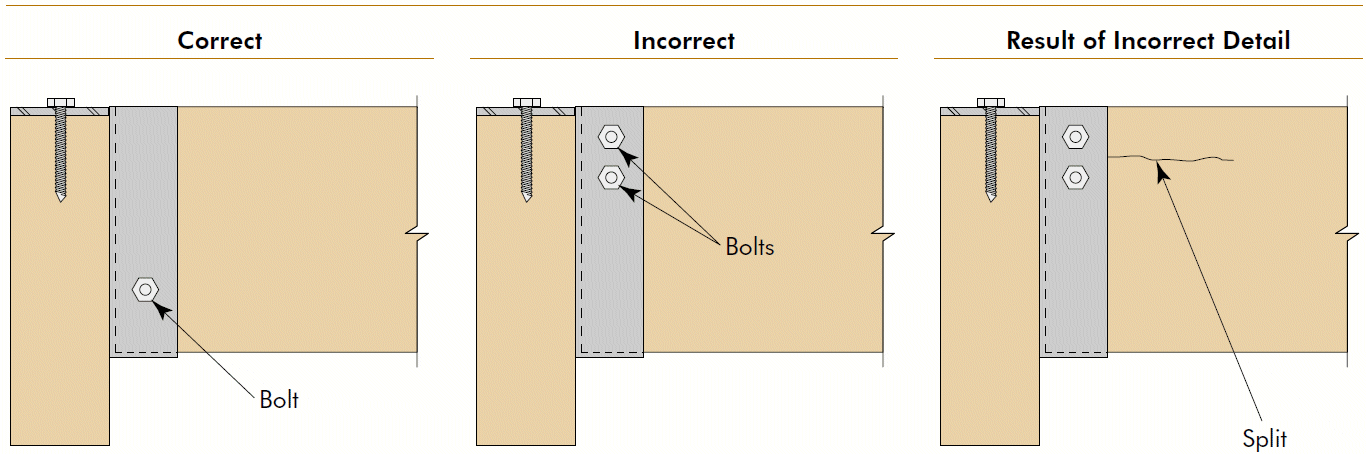
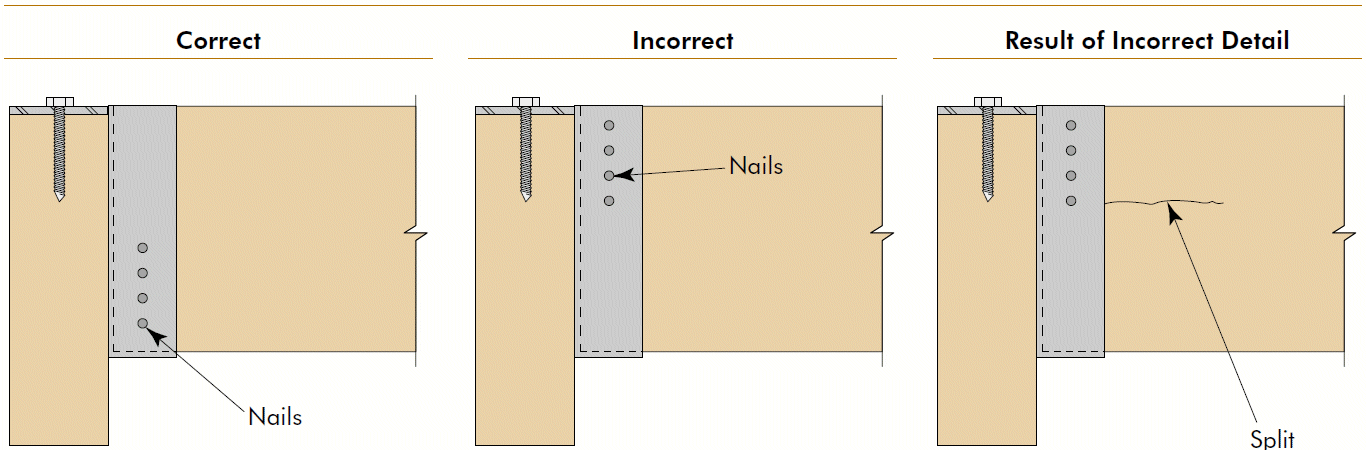
1. minimize across-the-grain distance between restraining elements 2. accommodate shrinkage and swelling 3. consider connection movement 4. principles apply to glulams AND sawn lumber, but importance increases with member size 5. transferring loads by compression ⊥ to grain is generally preferred6. cracks render bolts ineffective
References
1. Textbook
2. American Institute of Timber Construction (AITC) Publications
AITC 104 Typical Construction Details
Timber Construction Manual $105 (S&T library, 1985)APA The Engineered Wood Association T300 Glulam Connection Details
ASD-LRFD Manual section M10.4 Typical Connection Details
Example Connections
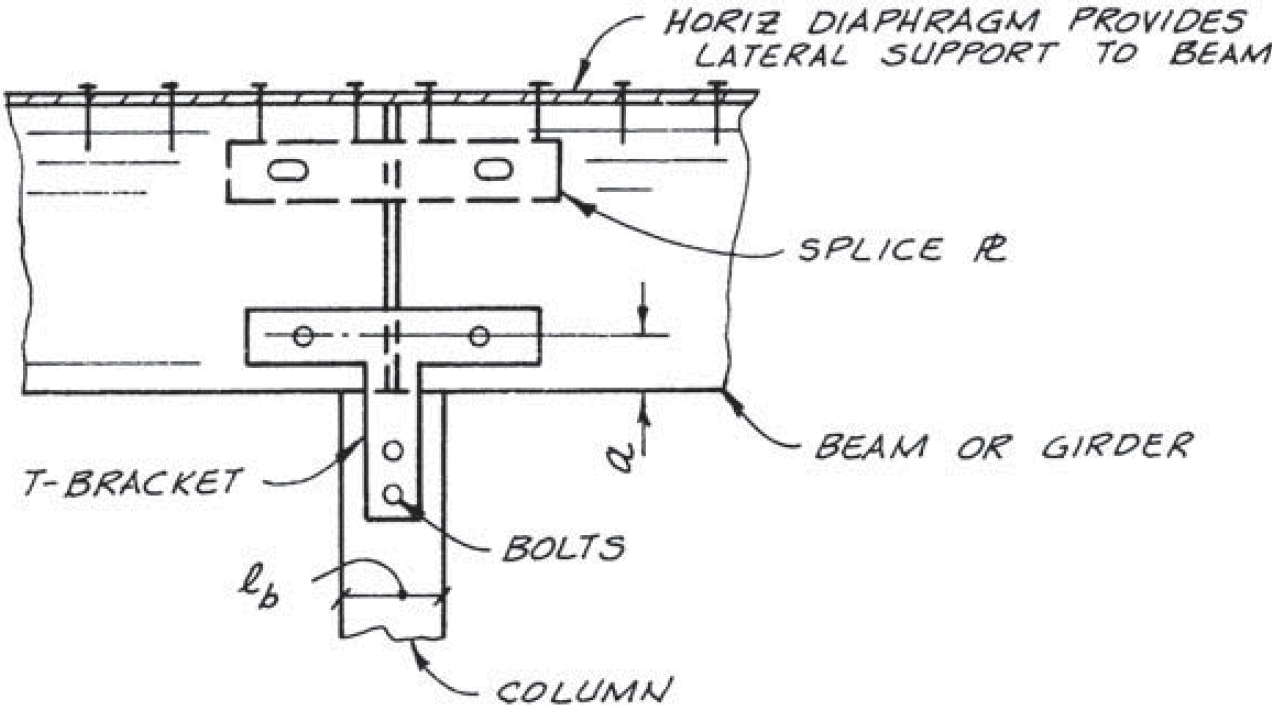
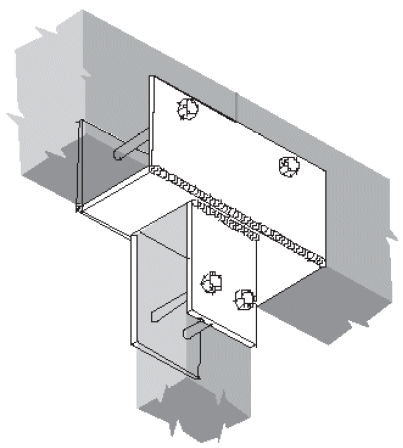
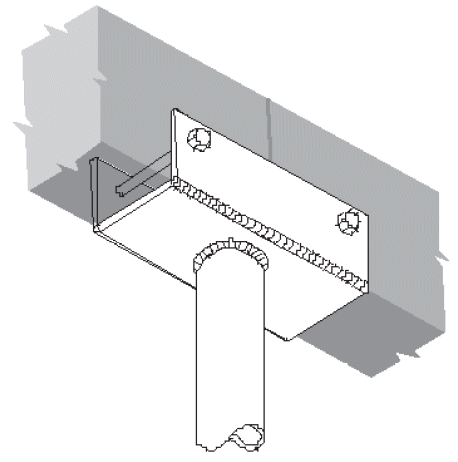
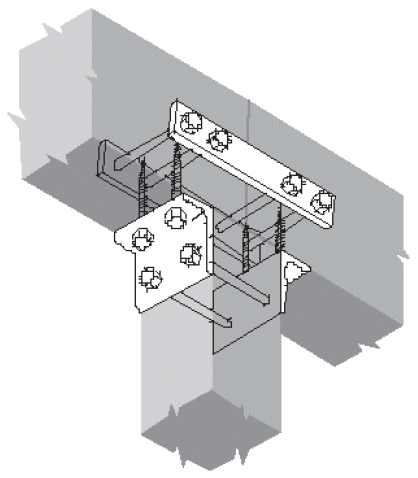
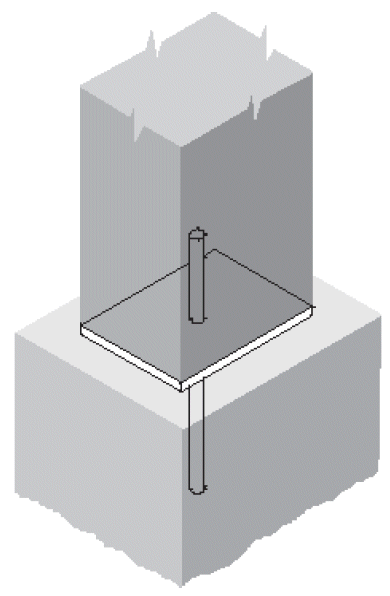
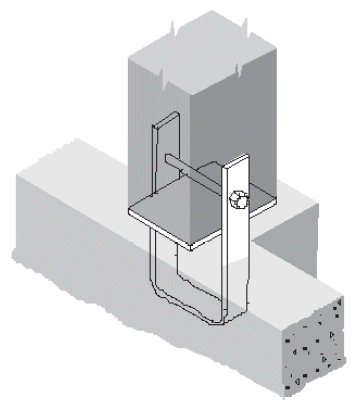
1. typical beam-to-column
a. tee
- example
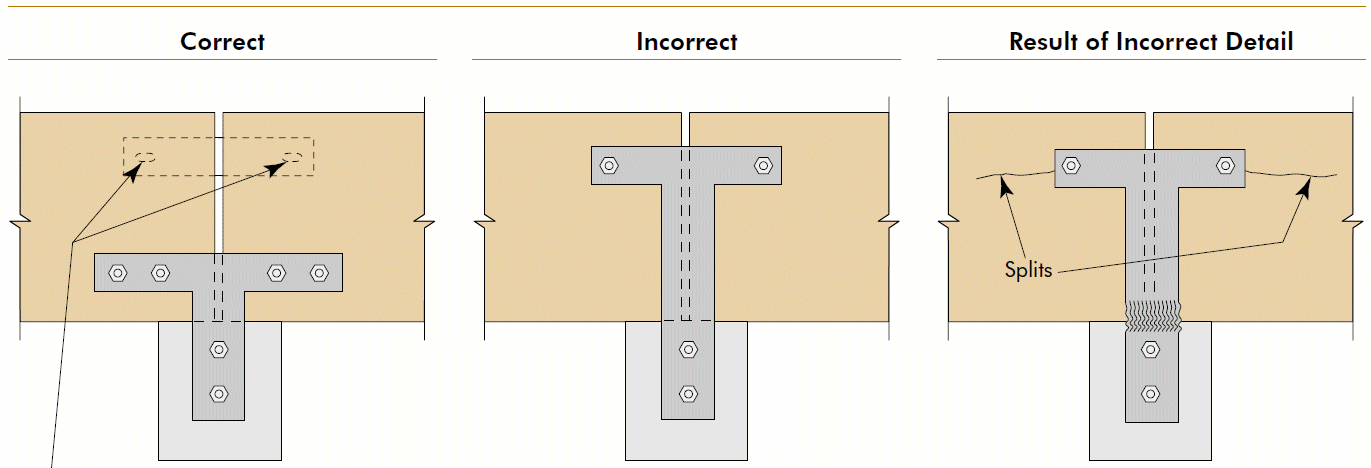
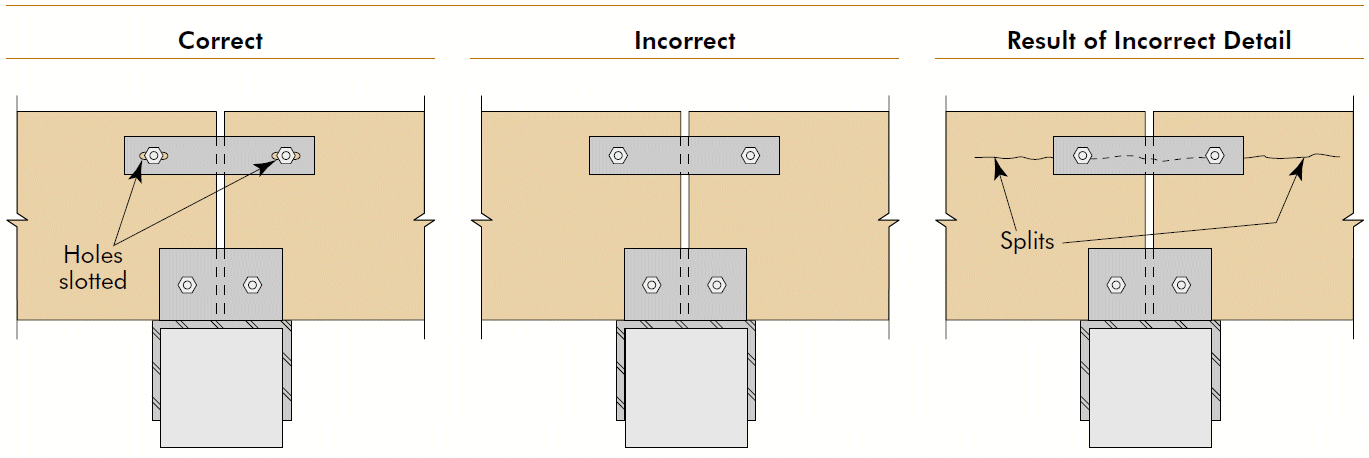
- cross-grain tension @ tee
- end rotation @ splice plate
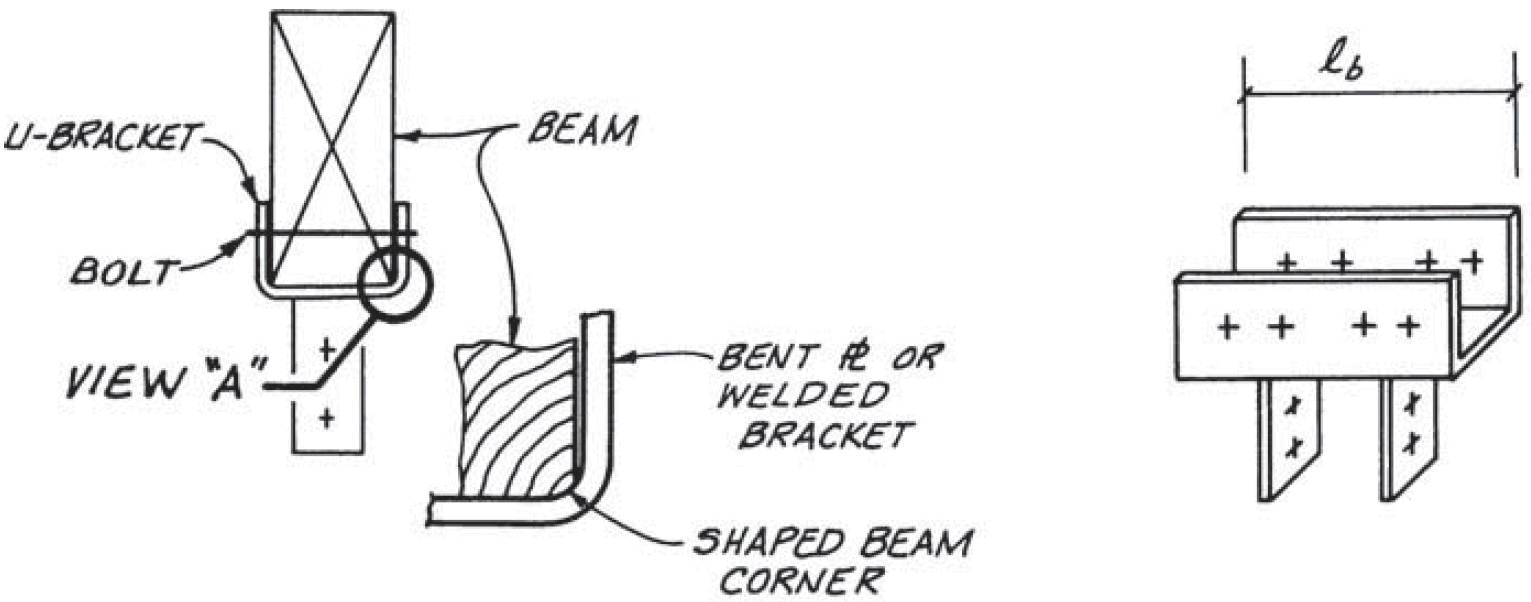
- shape corners for full seat
b. end
c. moment splice
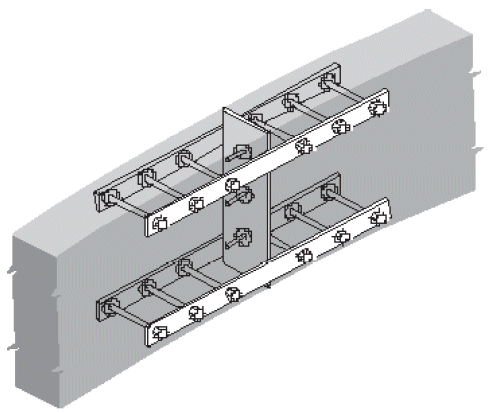
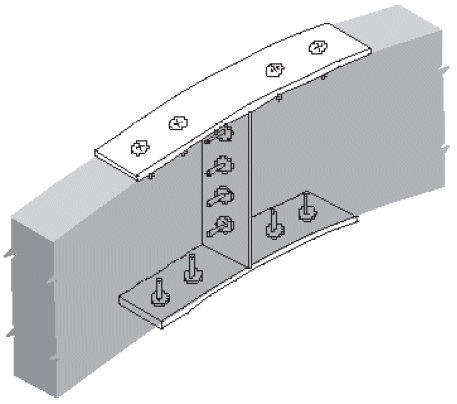
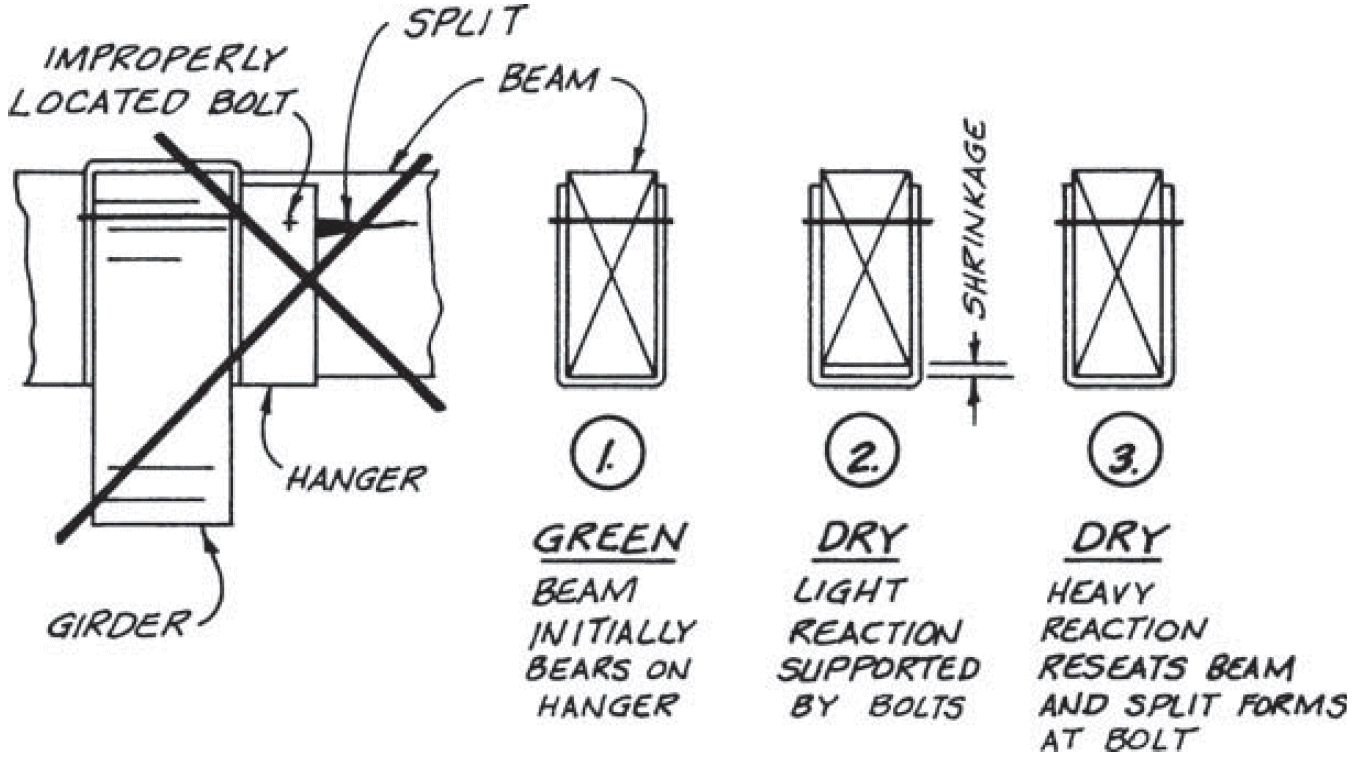
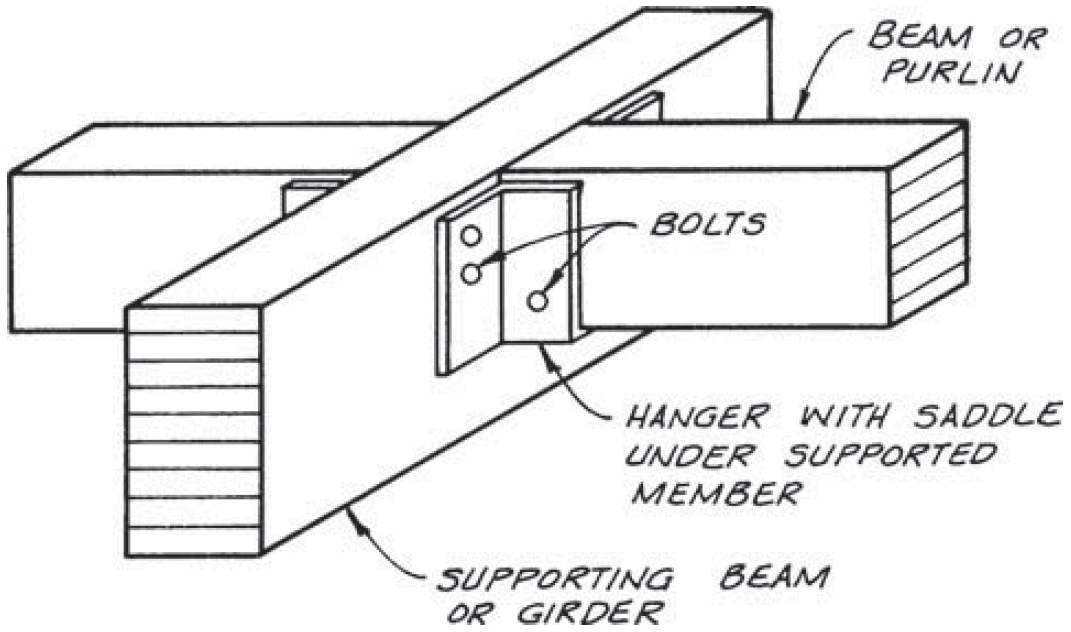
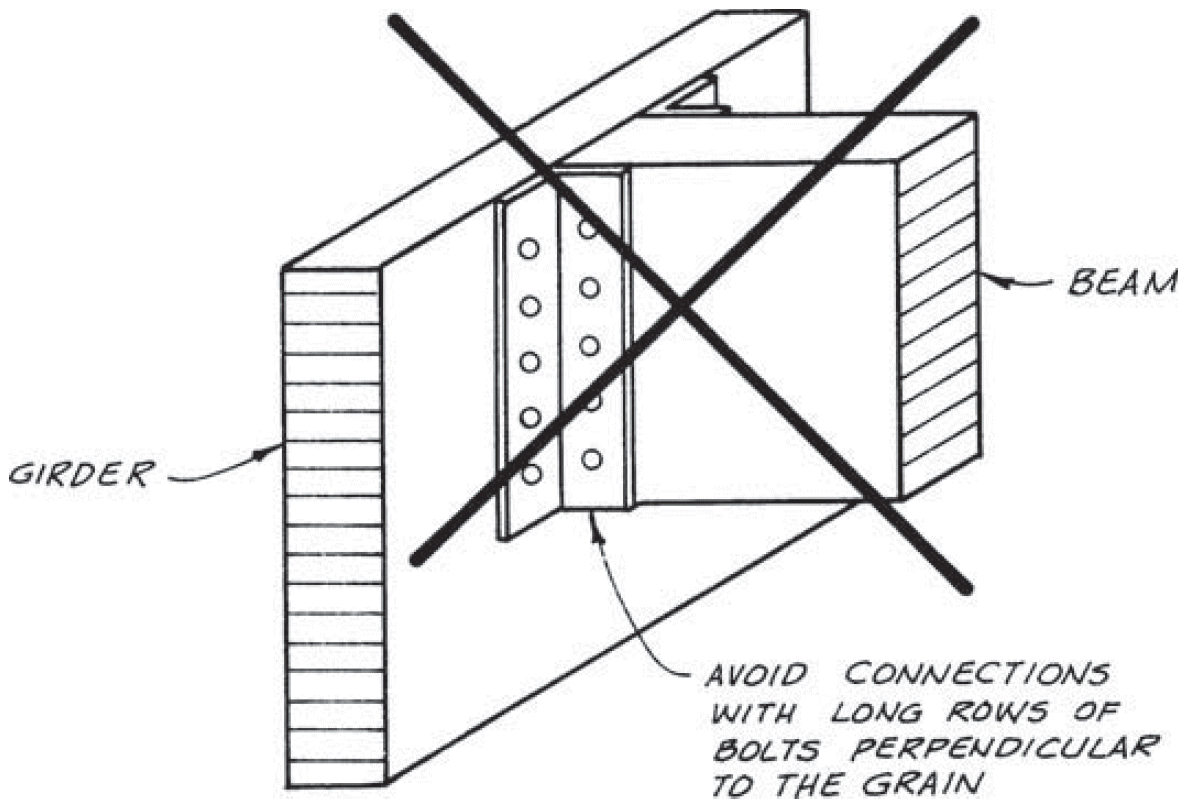
2. beam-to-girder saddle
- compression ⊥ to grain @ three spots
- different initial heights for shrinkage (flooring, sheathing)
- bolts near bearing points to minimize cross-grain tension
- avoid boring holes in high-quality outer lams
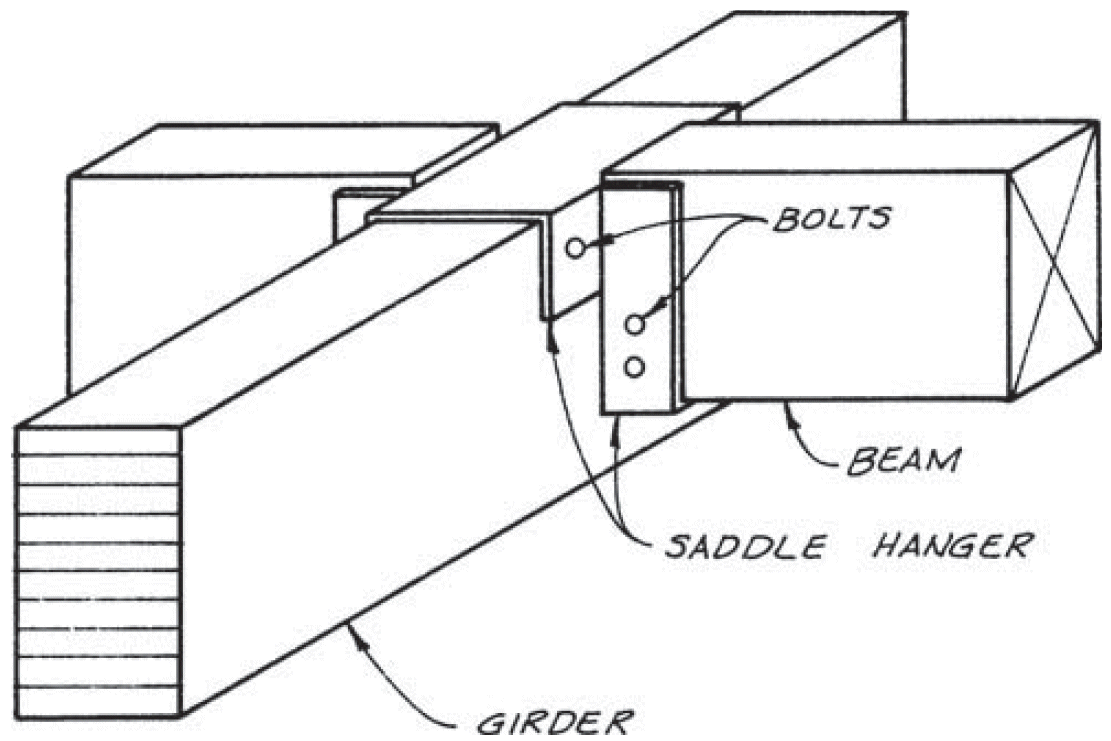
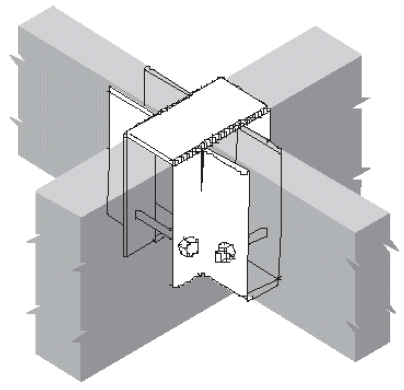
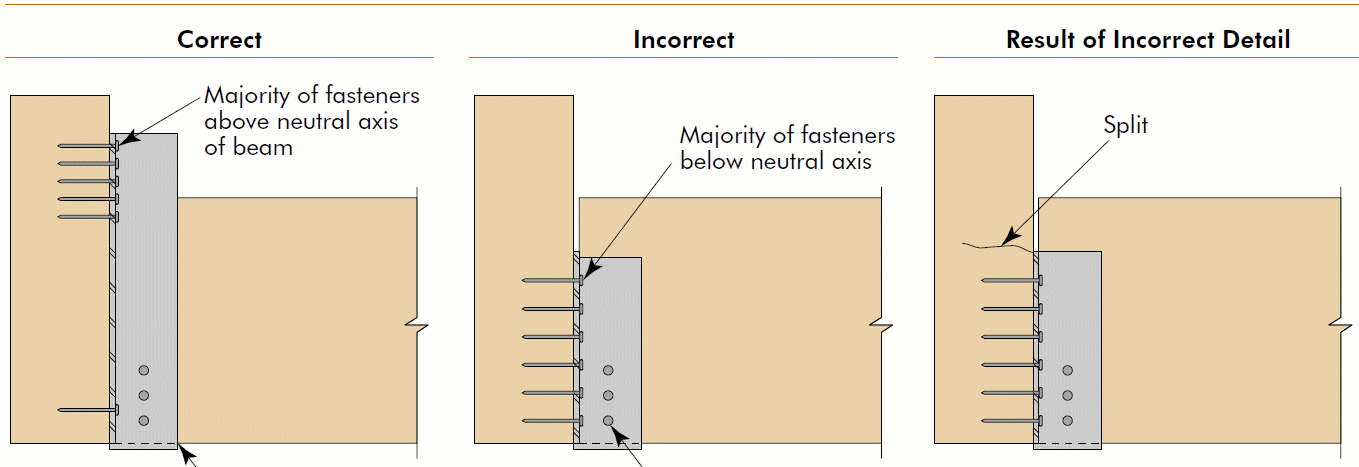
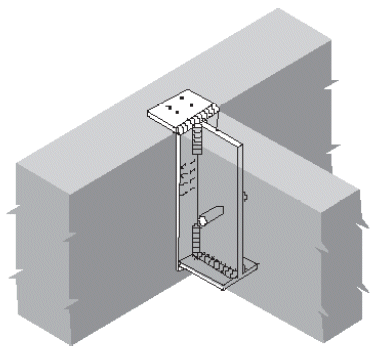
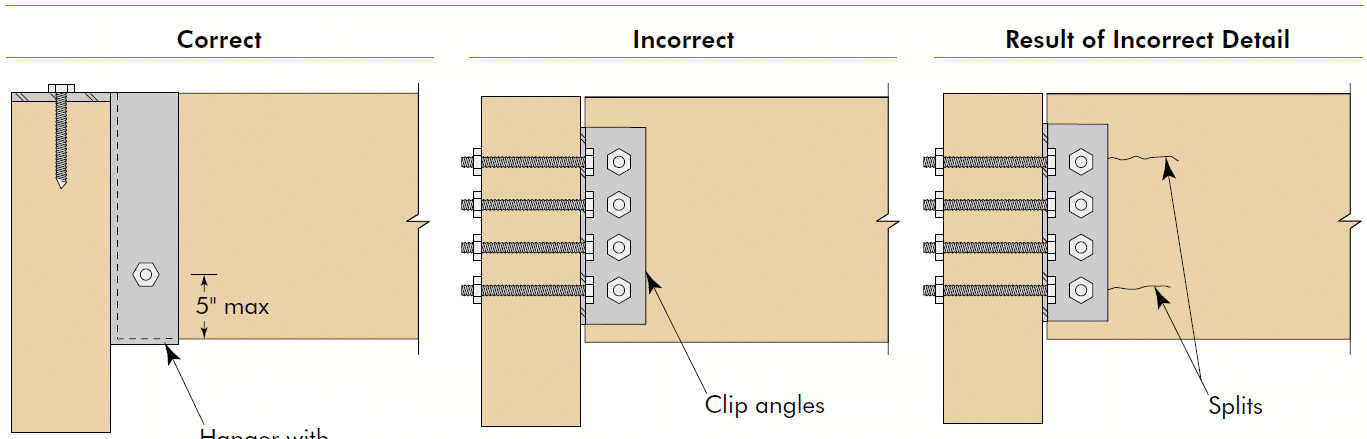
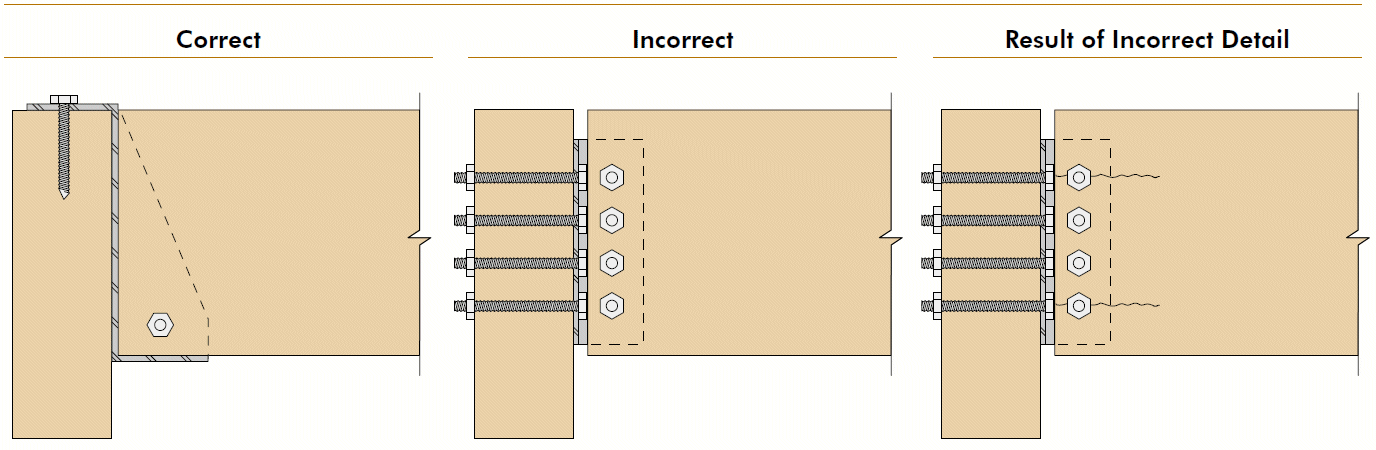
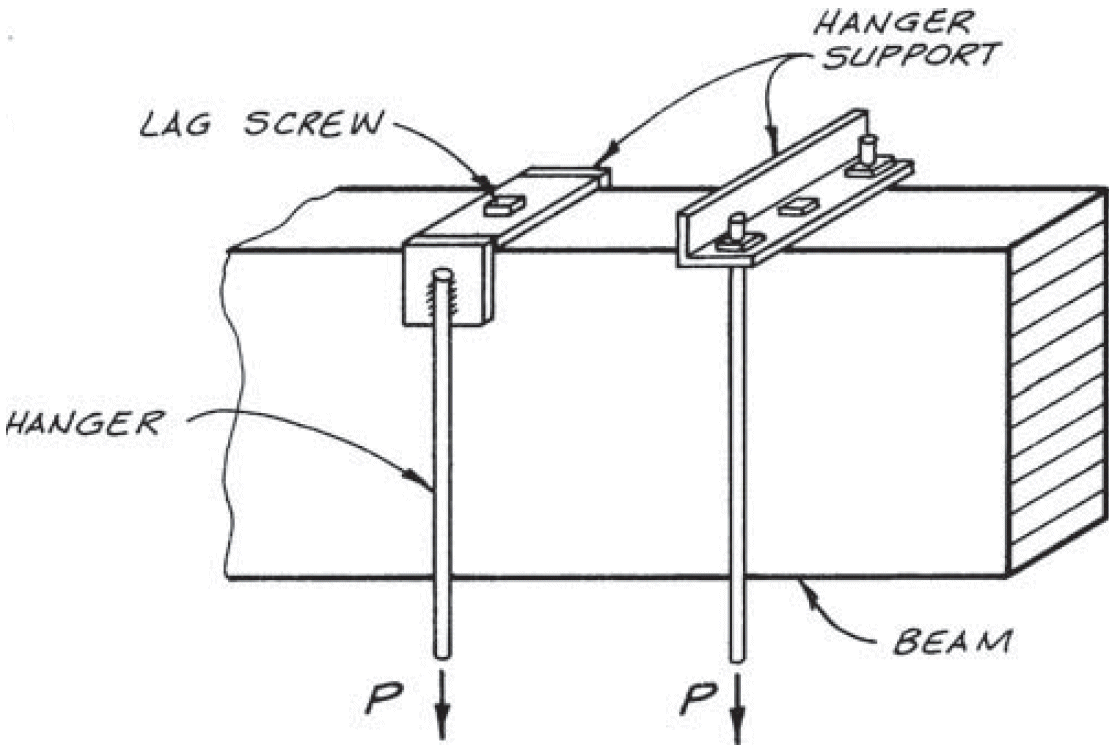
3. face hanger
- example
- example
- bolts in upper half of supporting beam, but not in extreme bending fibers, especially in cantilevers
- shear @ end of supported beam
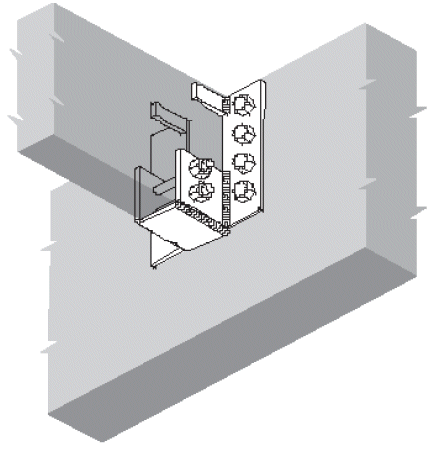
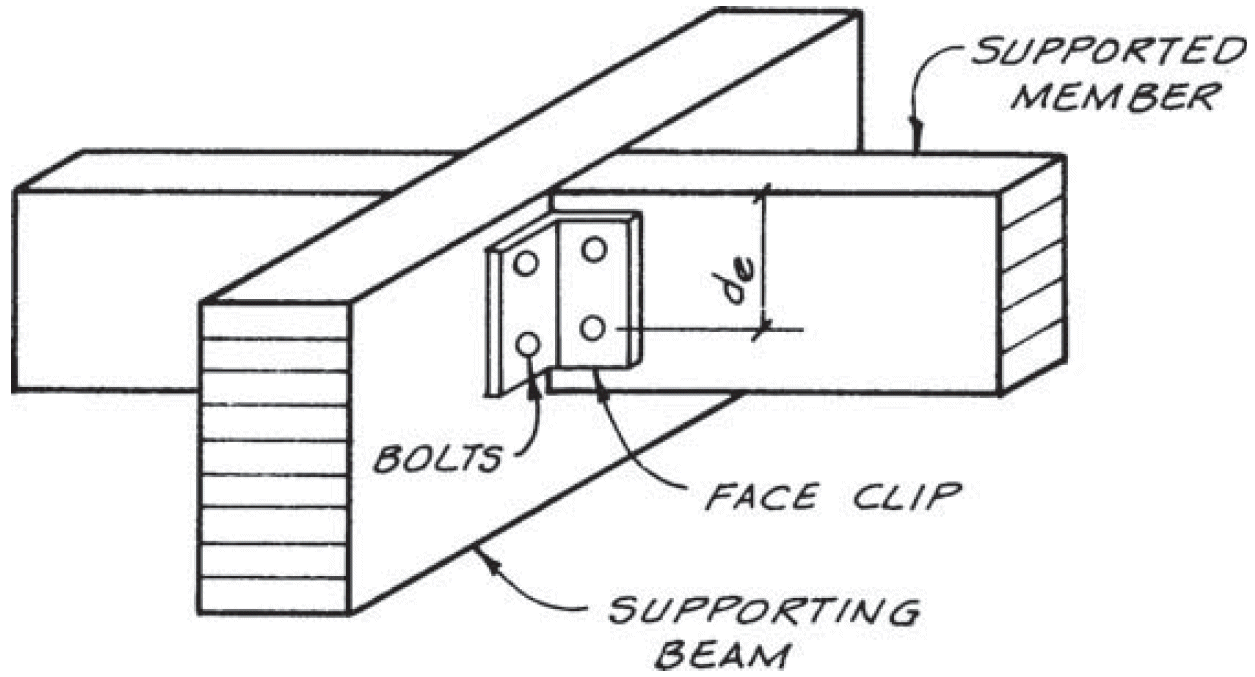
4. face clip
- no compression ⊥ to grain (only for light loads)
- cross-grain tension
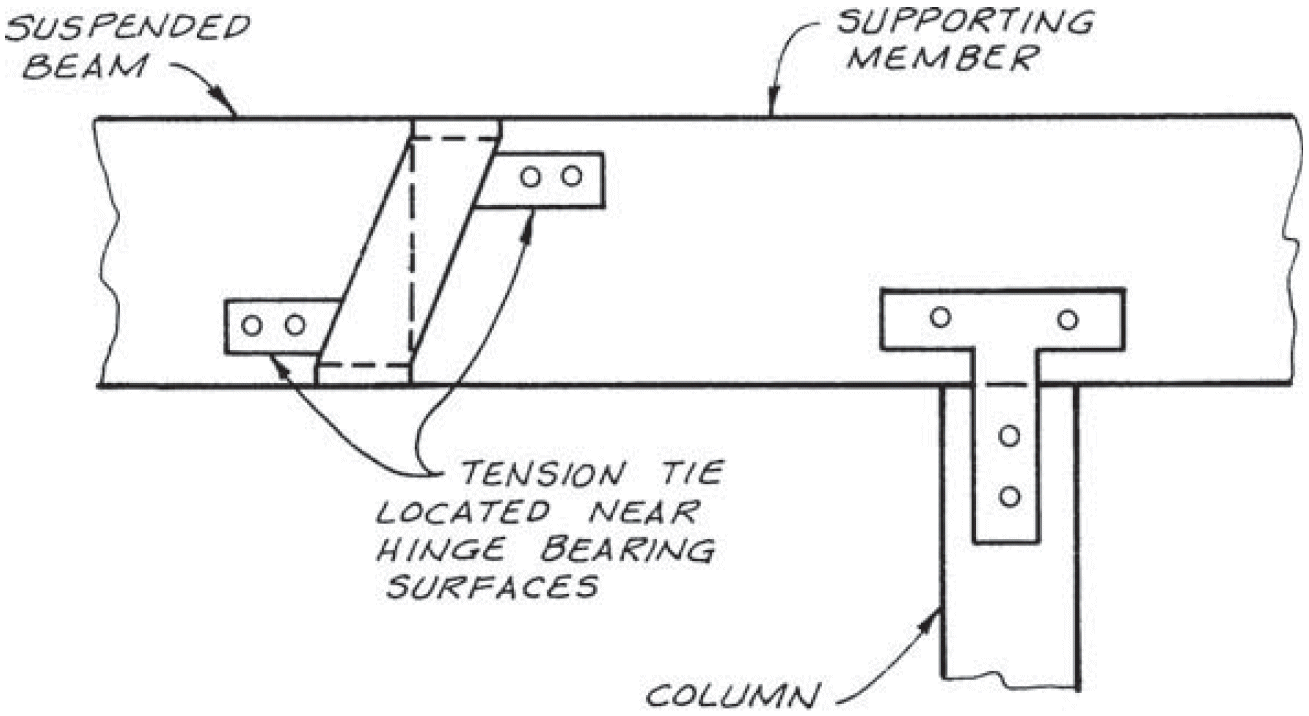
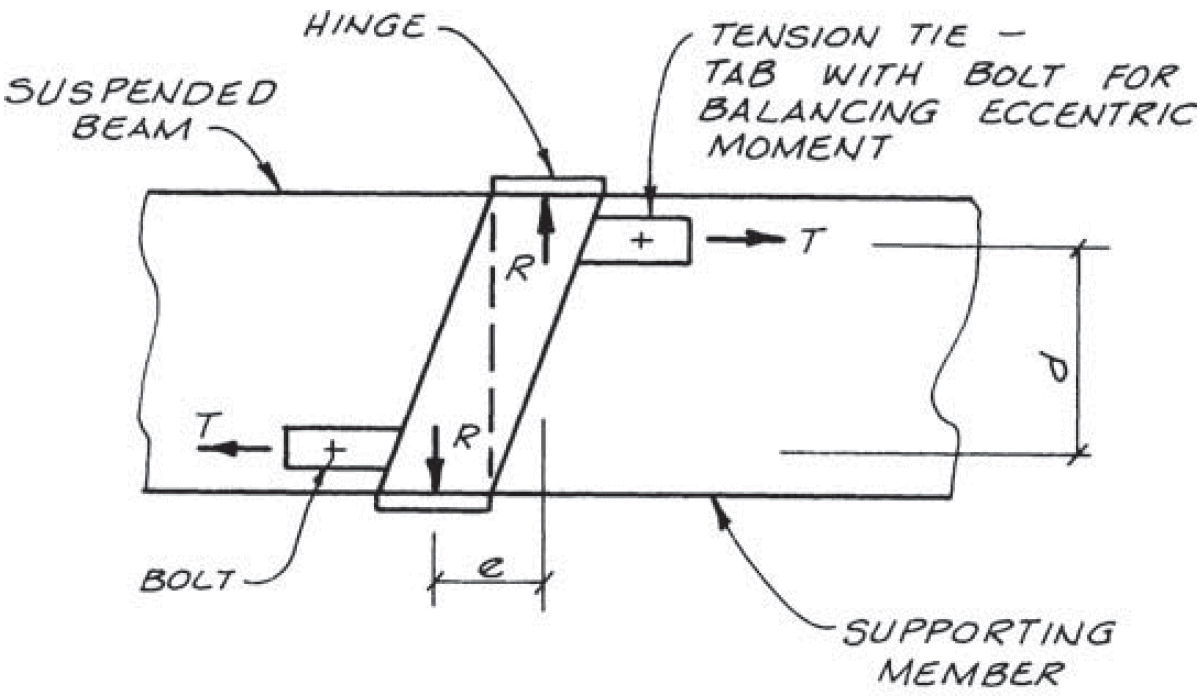
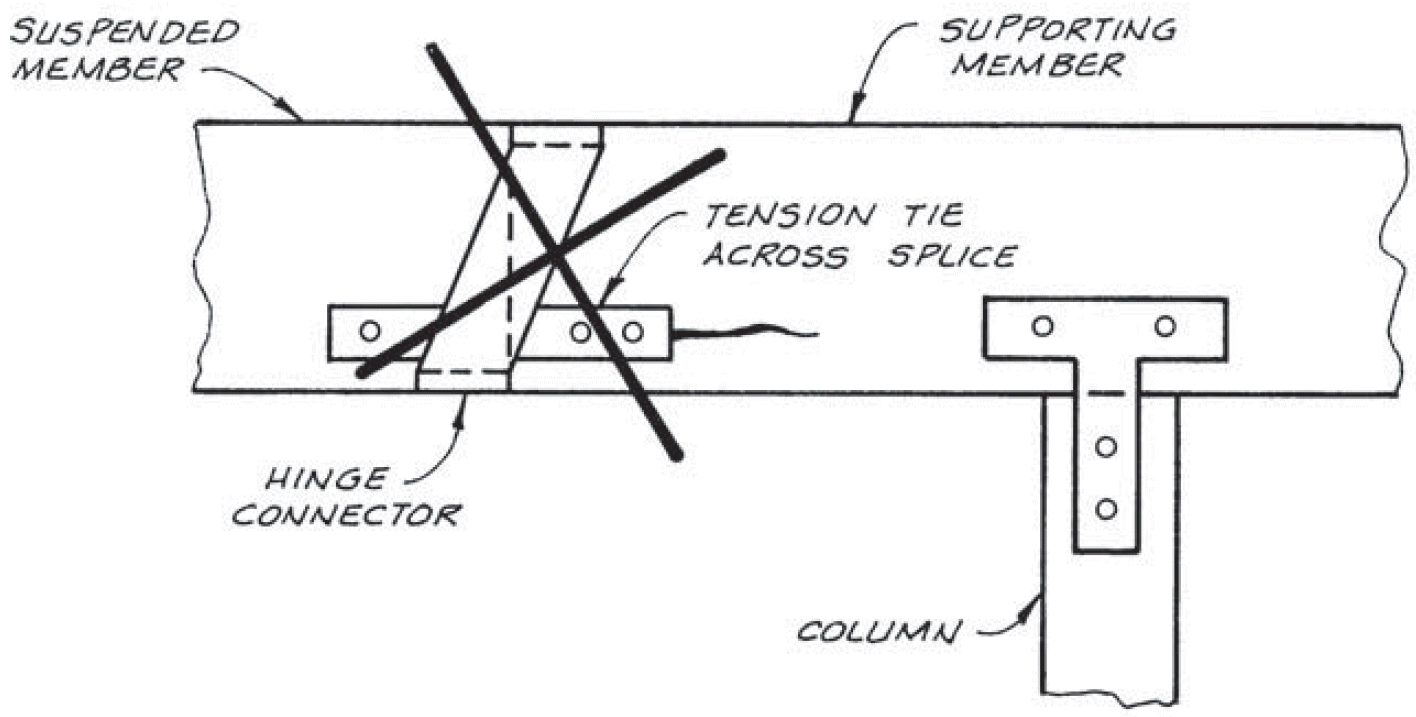
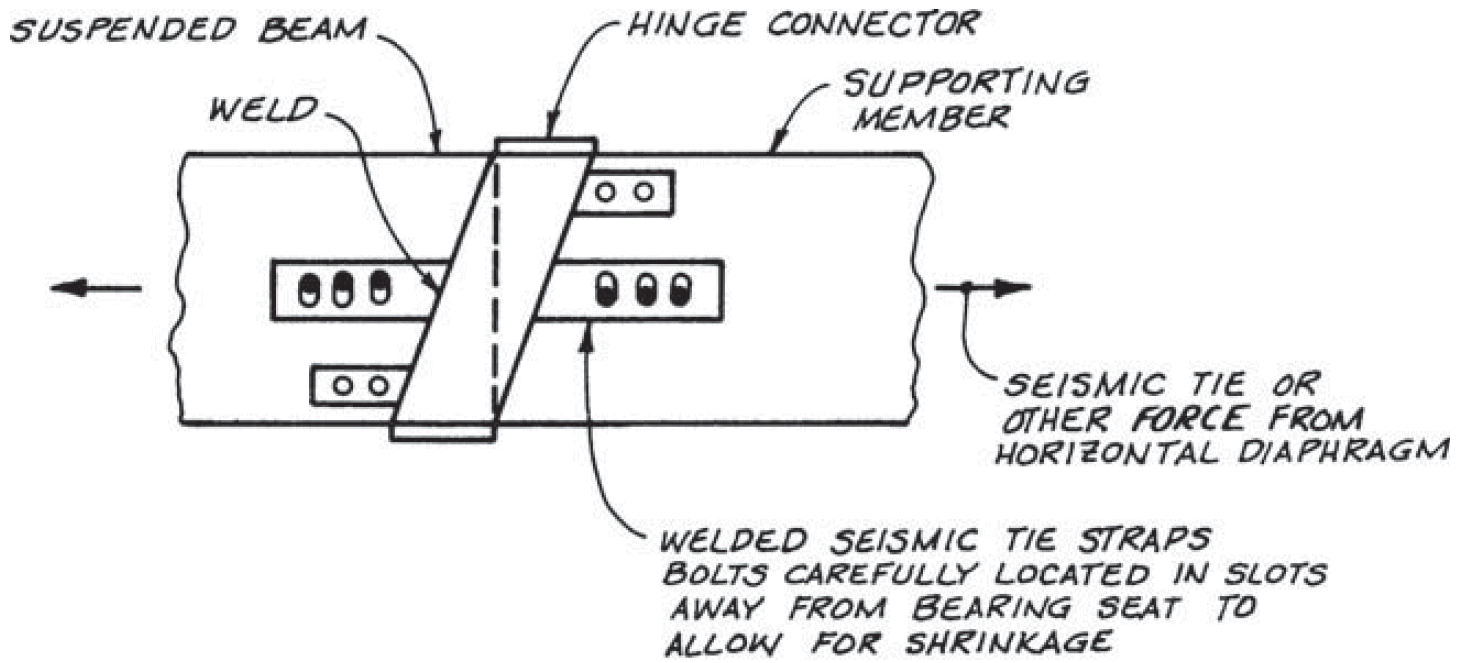
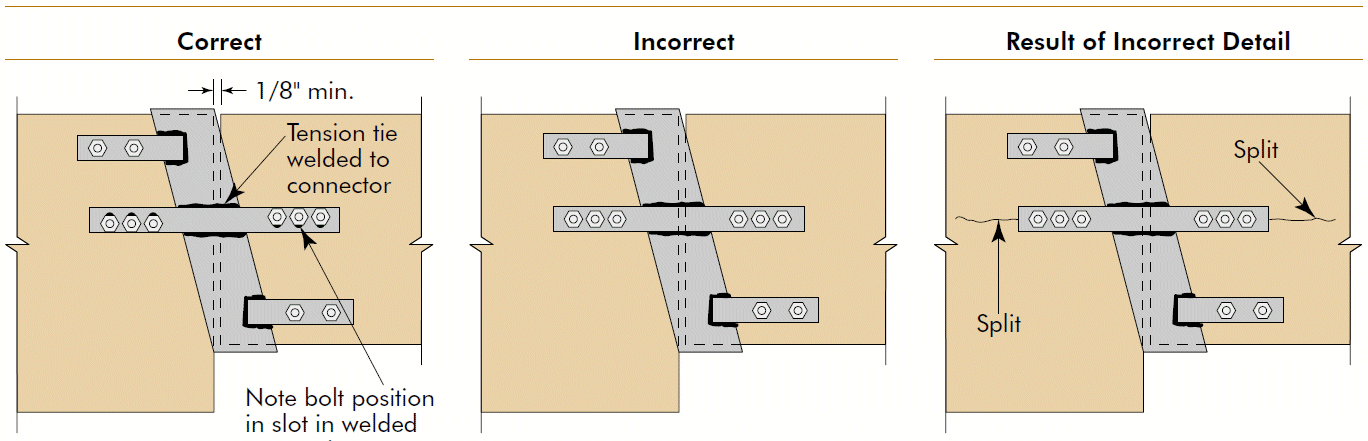
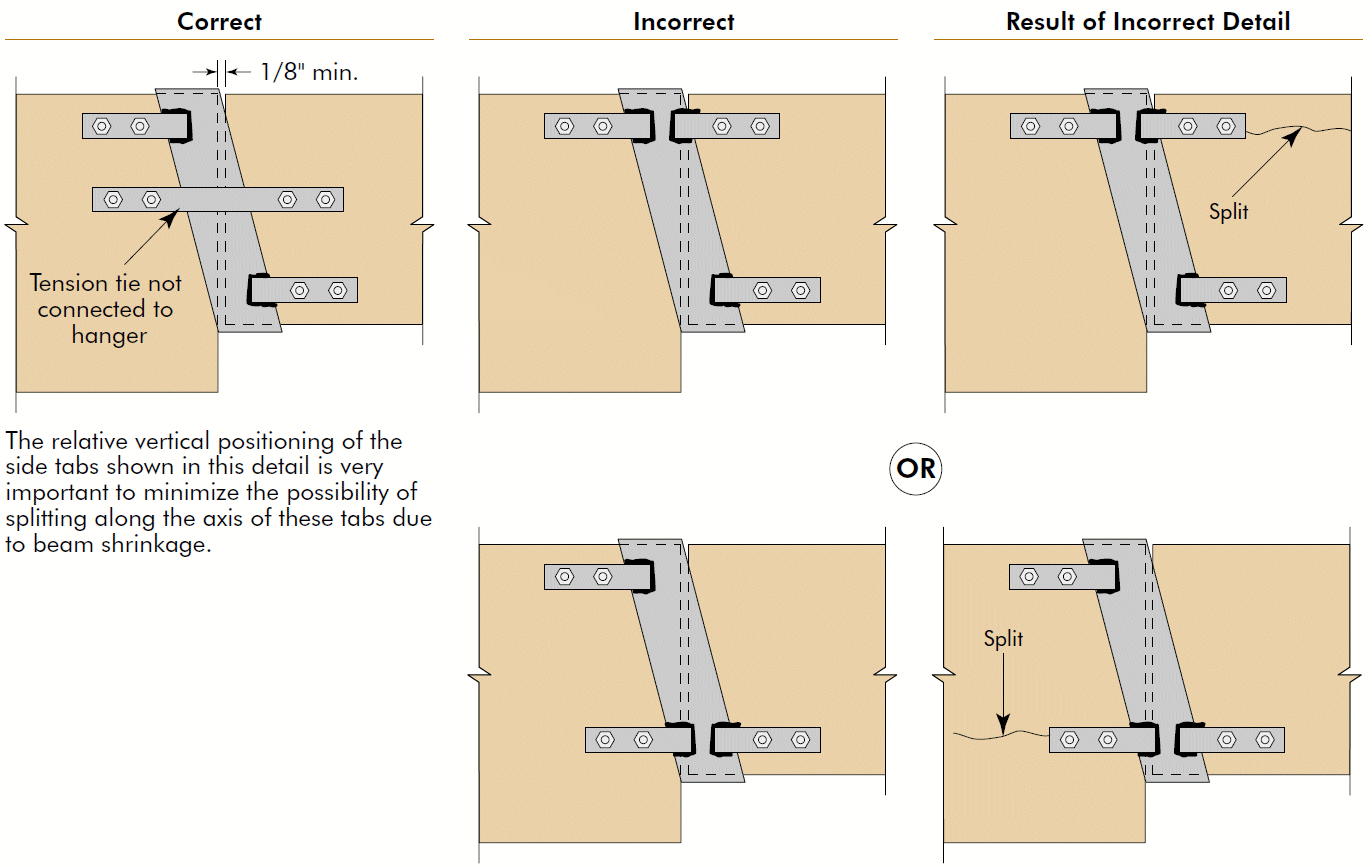
5. cantilever hinge
- section 6.17
- see second photo
- example
- example
- problems
- compression ⊥ to grain @ bottom of supported beam
- compression ⊥ to grain @ top of supporting beam
- 2X vertical movement with shrinkage
- joint rotation
- fixes
- balance the eccentric moment
- note bolt location in slots
- separate splice plate at mid-depth if needed
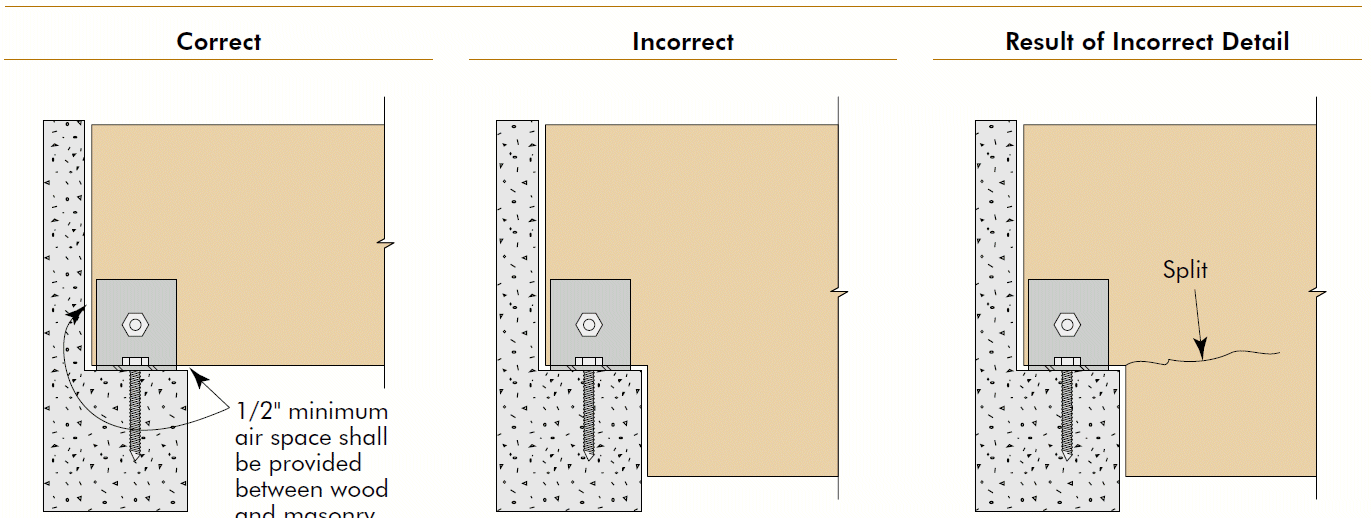
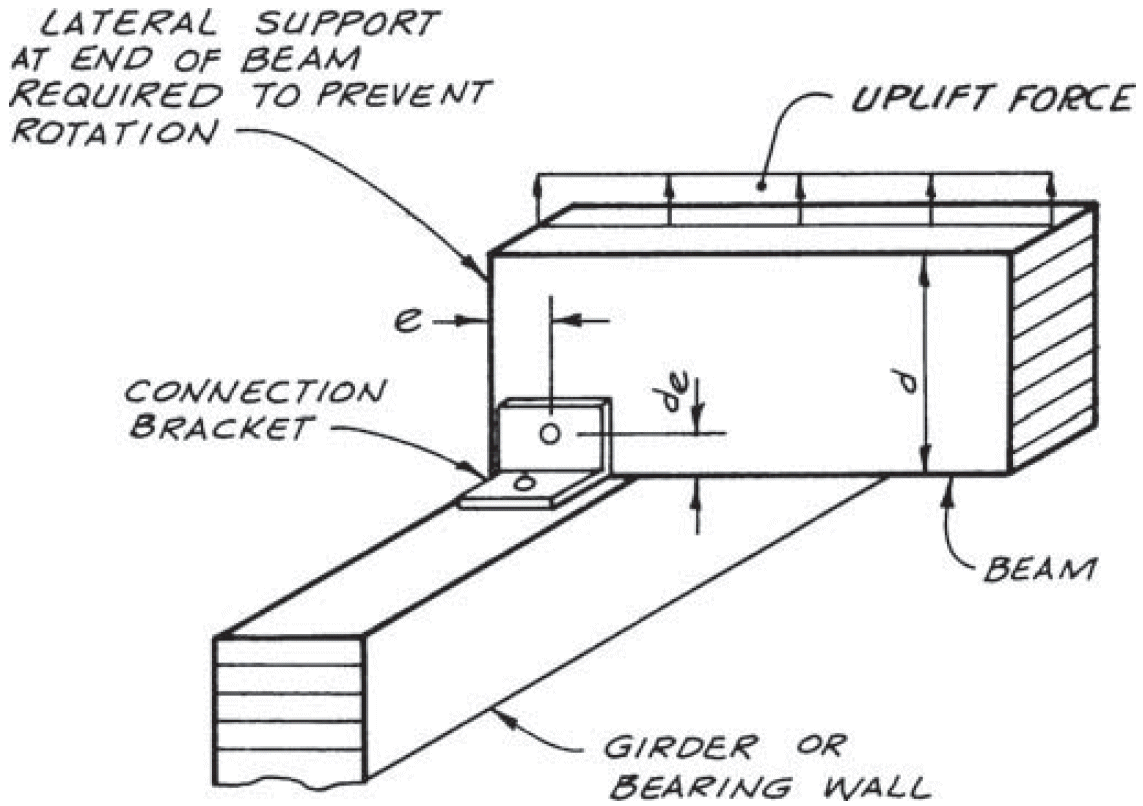
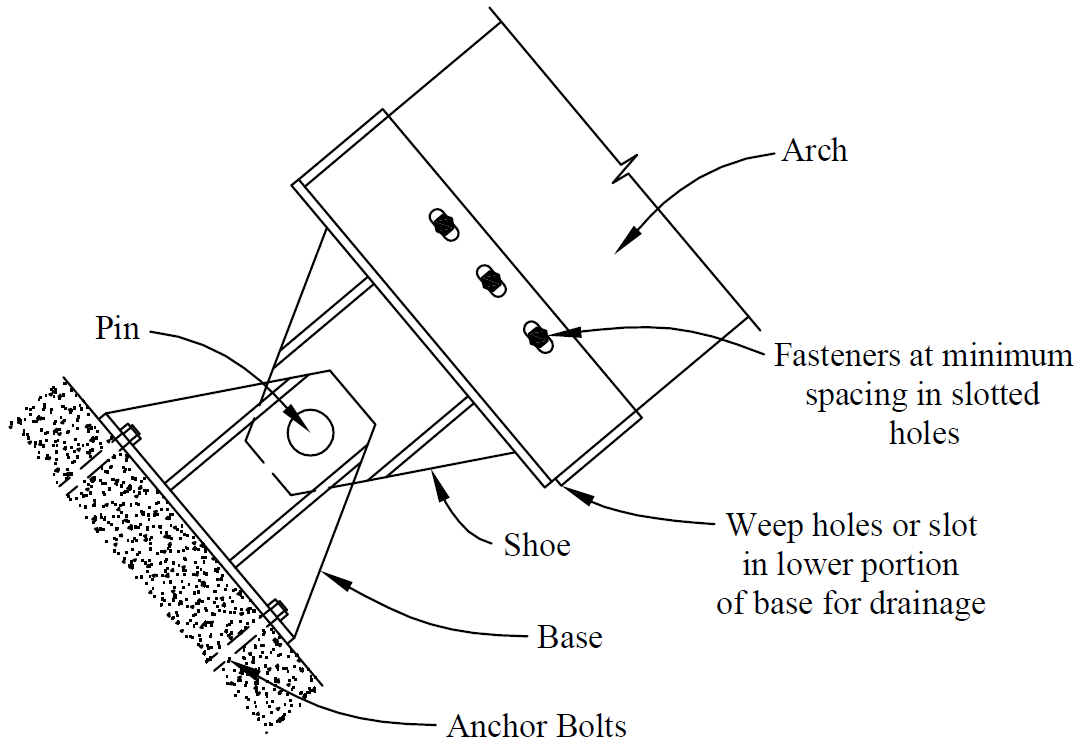
6. uplift
- compression ⊥ to grain
- edge distance
- shear stresses due to uplift
- end distance
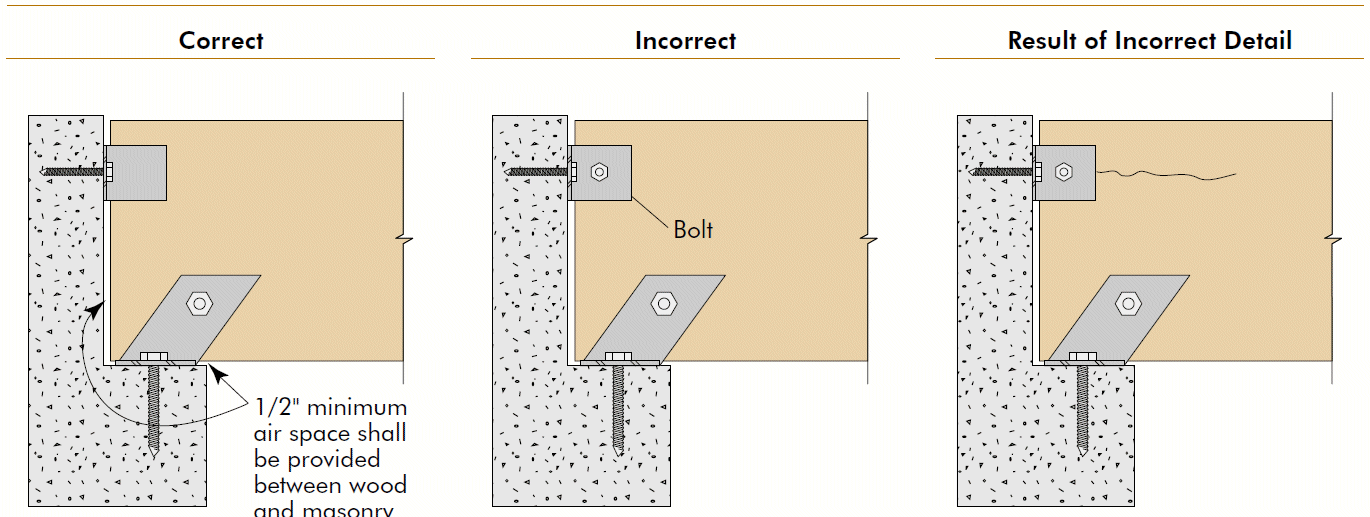
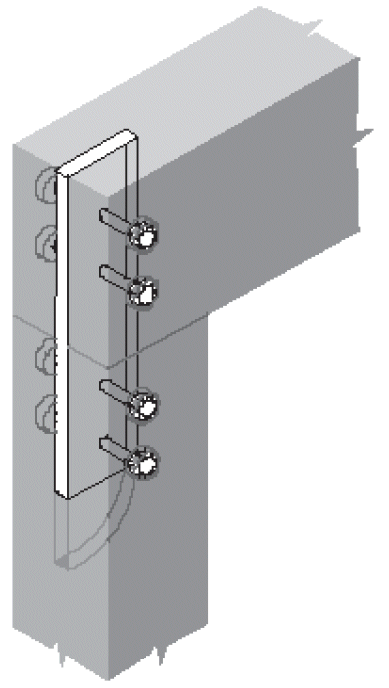
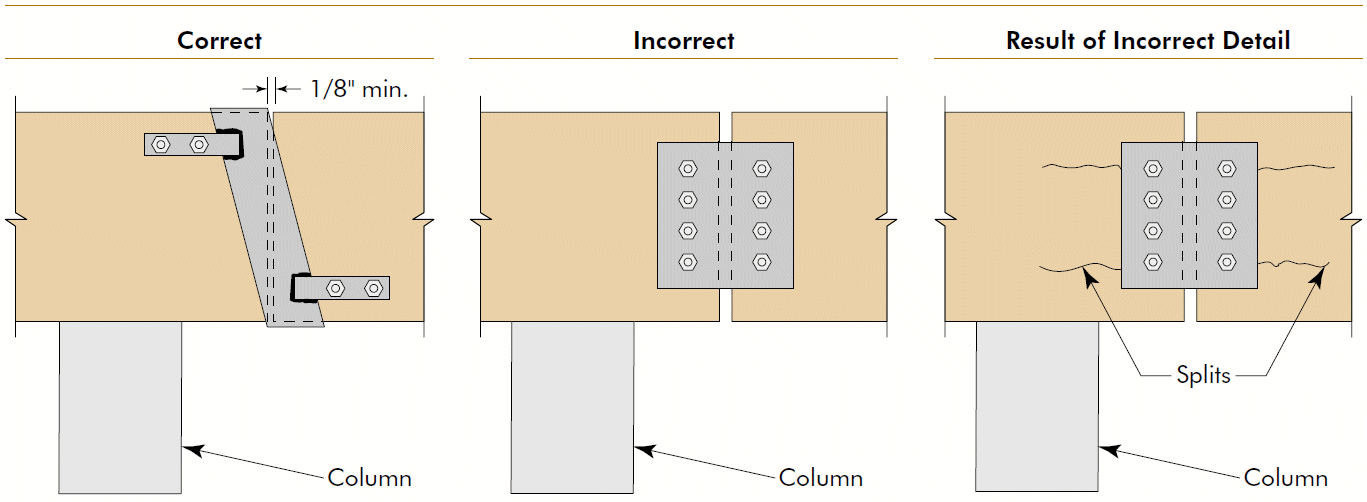
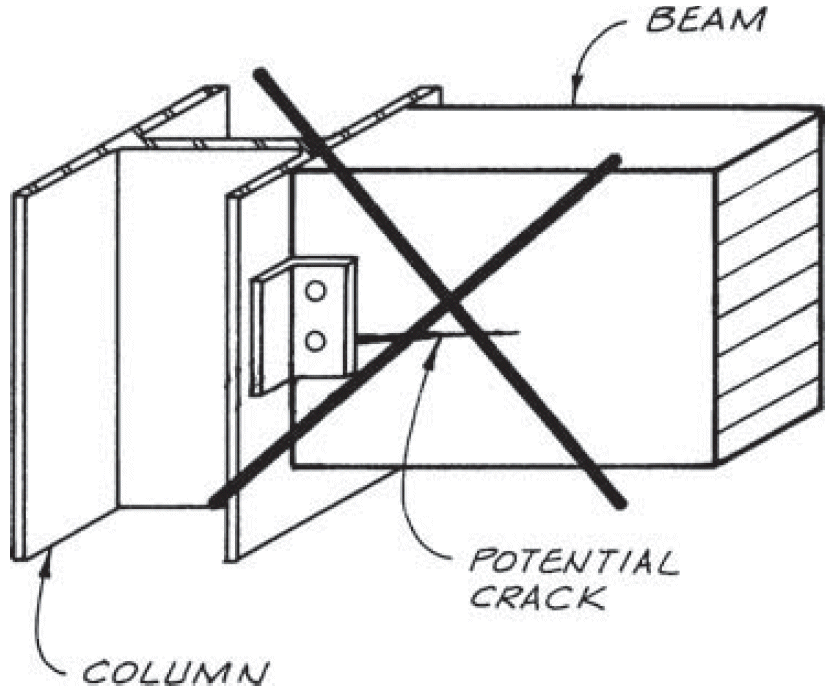
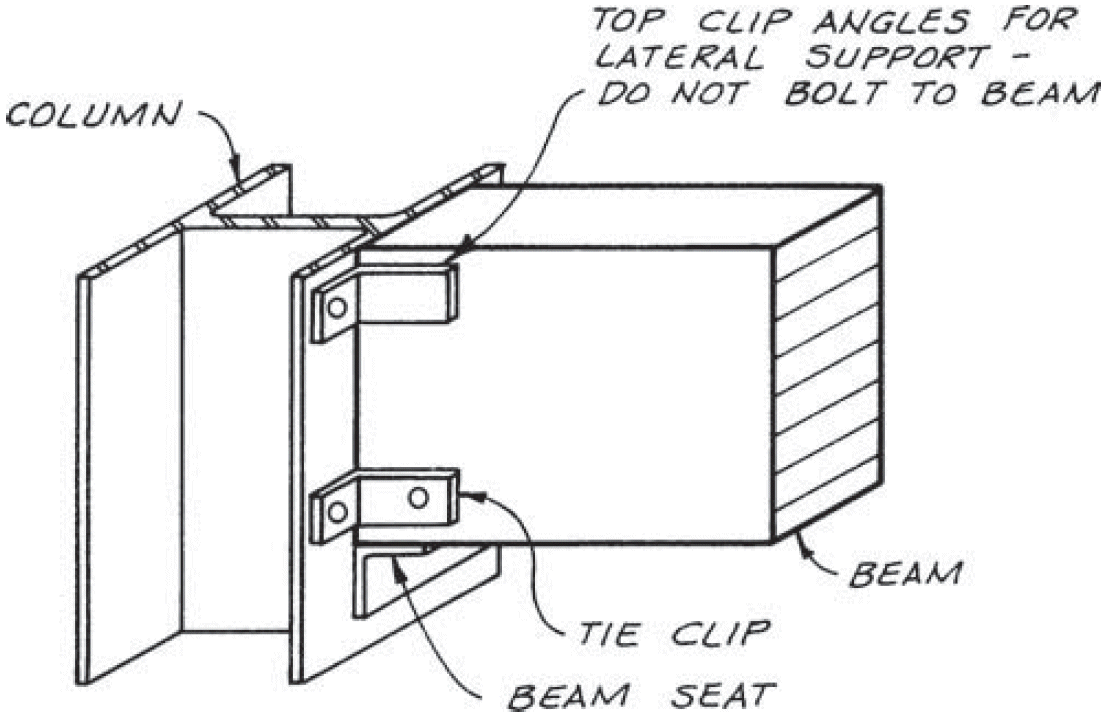
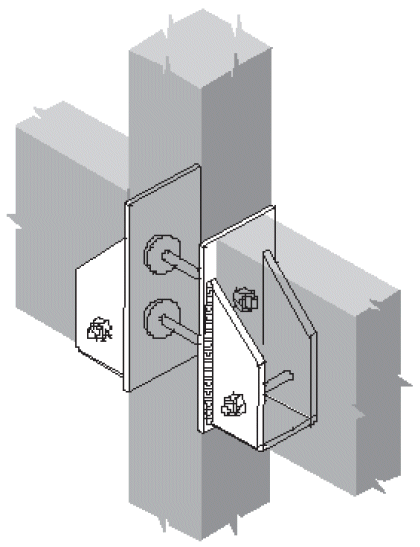
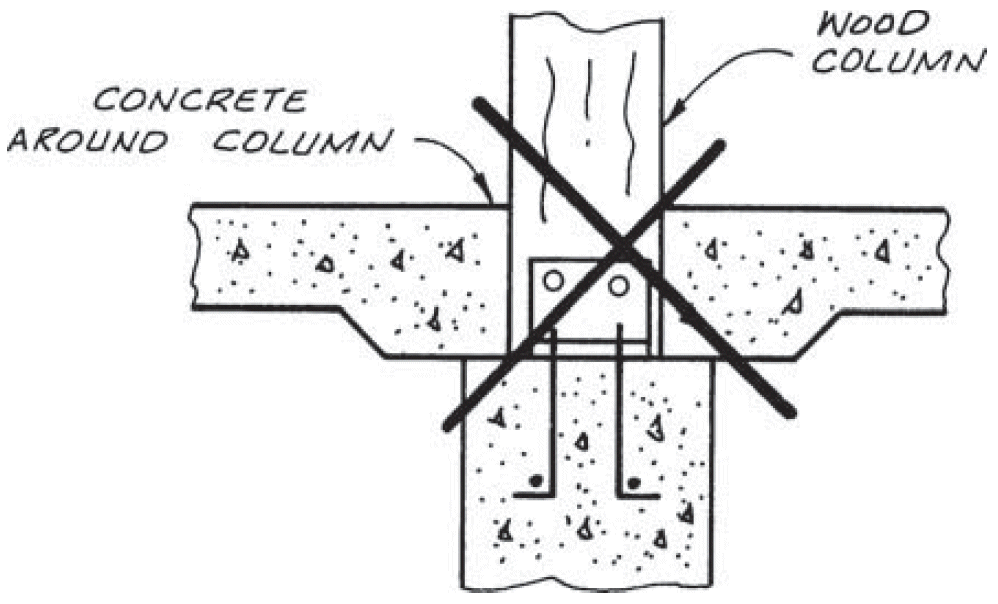
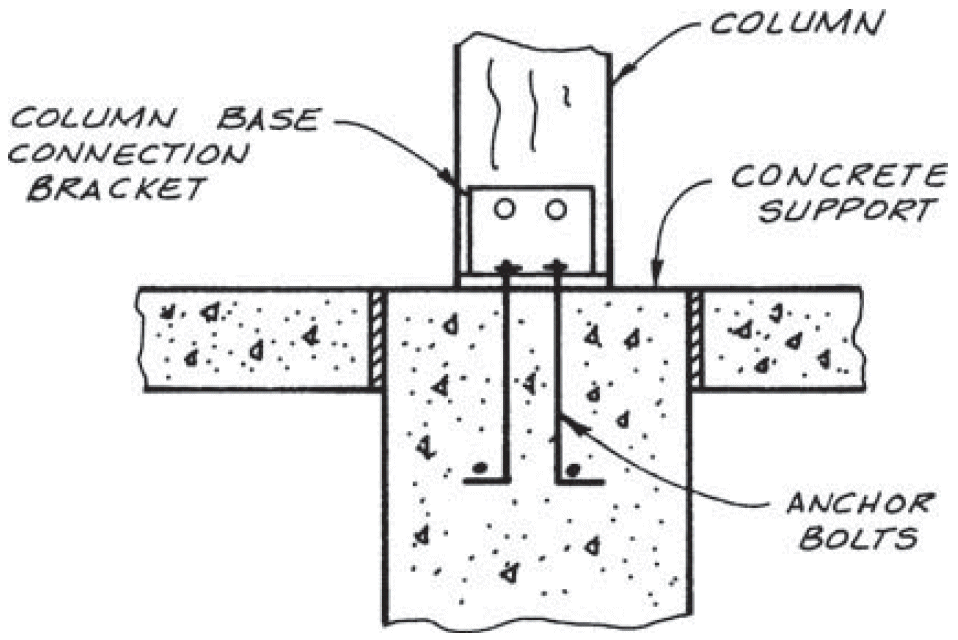
7. beam to continuous column
- problems
- cross-grain tension
- horizontal shear
- fix
- compression ⊥ to grain @ beam seat
- tension + rotation @ tie clip
- lateral stability @ clip angle
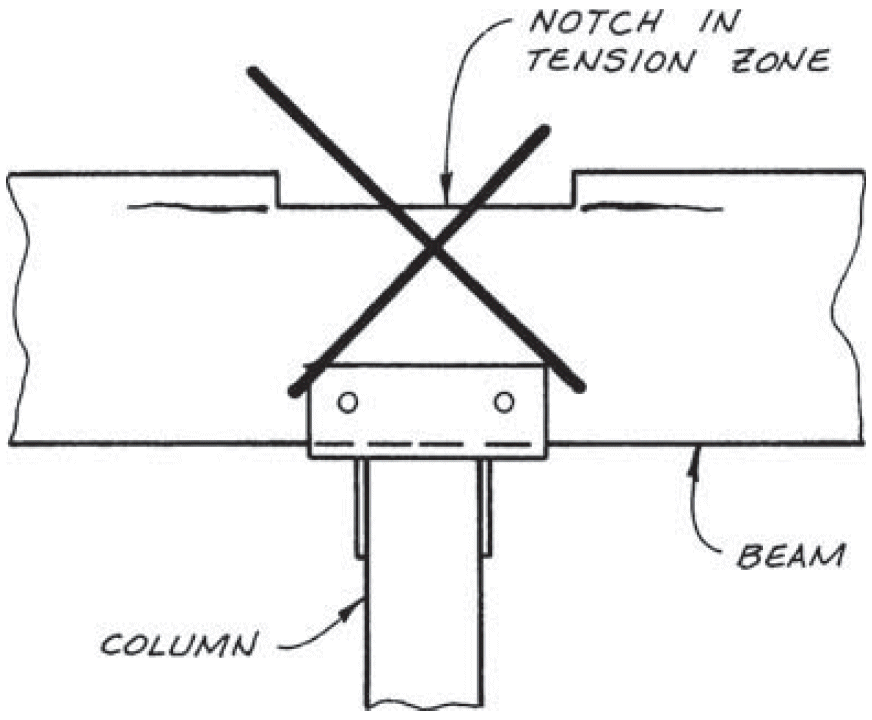
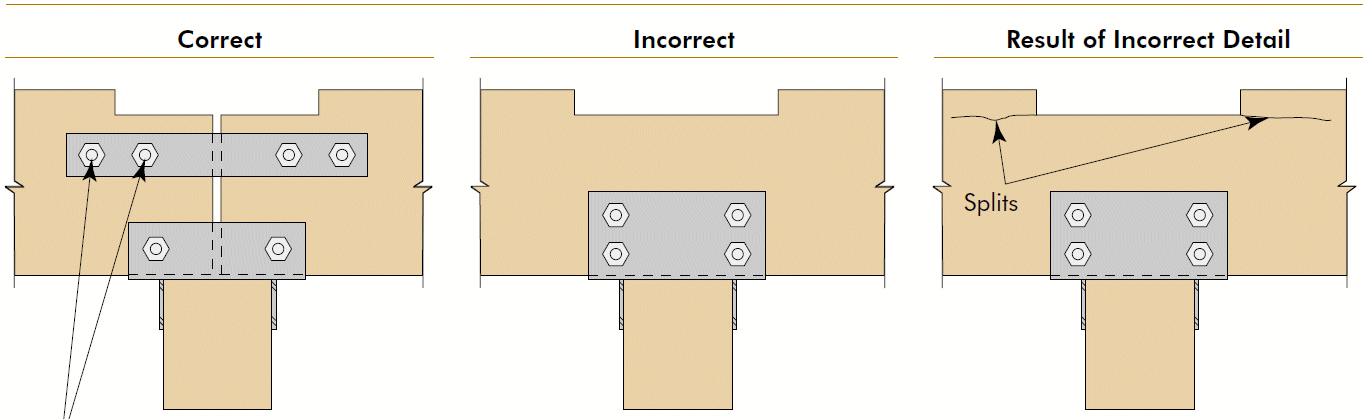
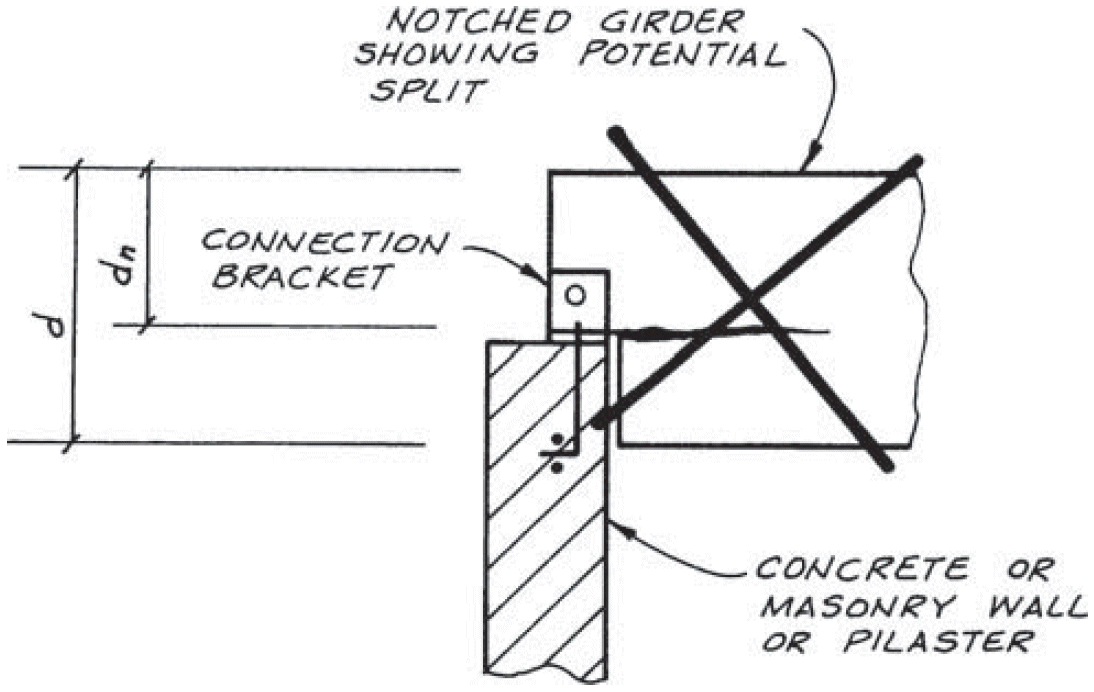
8. notch in tension side
- recessed for connection hardware, conduit, etc.
- renovation
- don't know original intent
- details covered up
- problems
- fix
- avoid
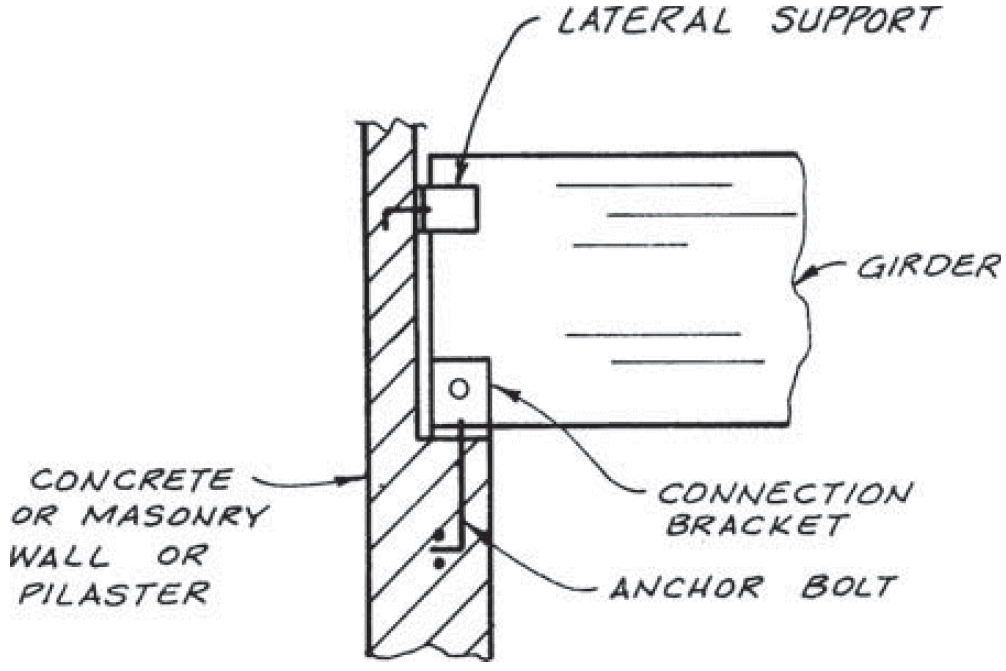
9. end notch
- problems
- reduced shear strength
- stress concentration
- exposure of end grain (non-uniform drying)
- fix
- lower connection
- add lateral support
- APA EWS S560 Field Notching and Drilling of Glued Laminated Timber Beams
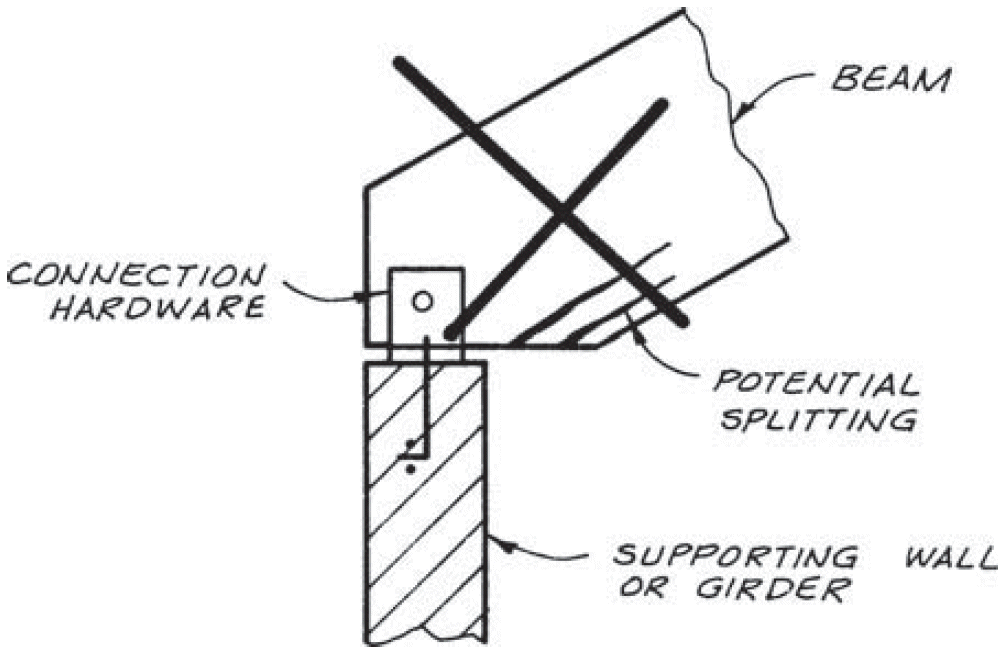
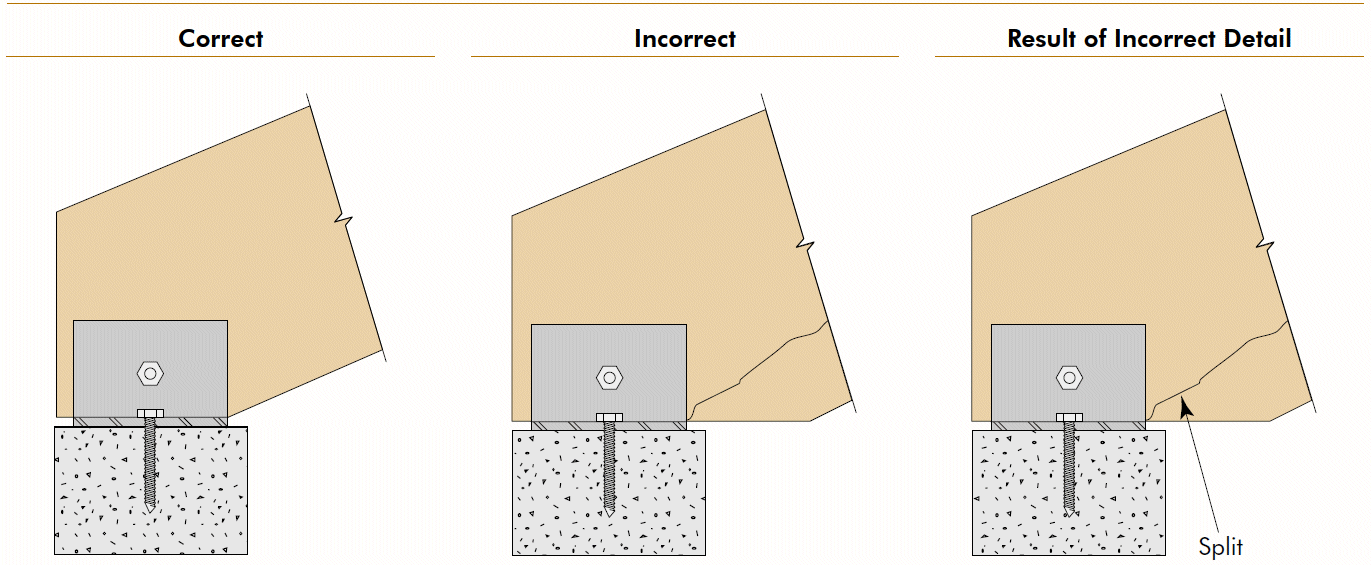
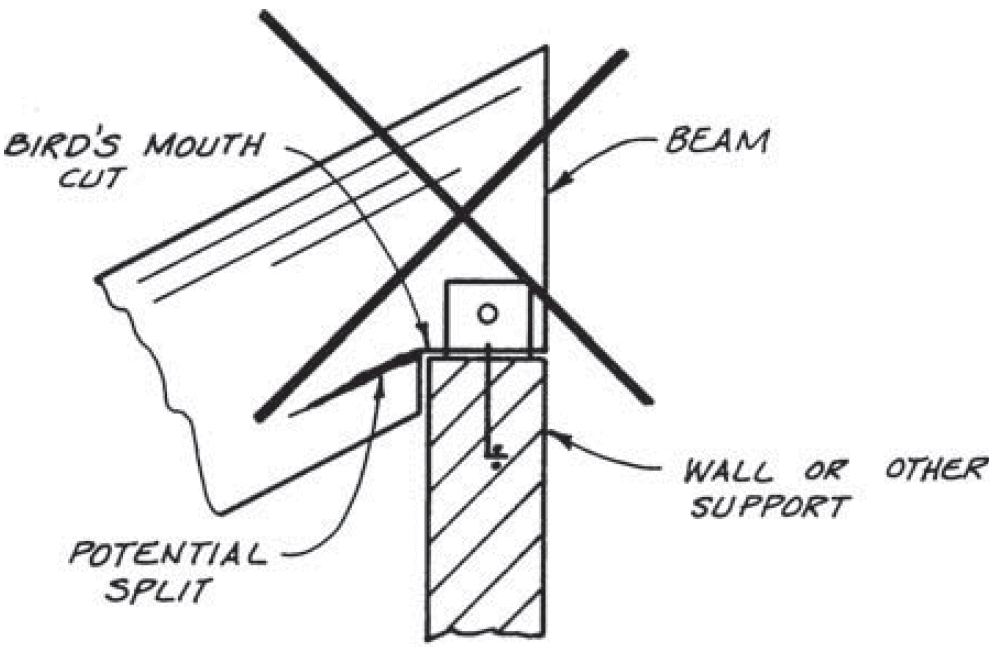
10. inclined beam - lower support
- similar to notch
- problems
- shear strength
- exposed end grain on tension side
- fix
- lower connection
- bearing on tapered cut
- exposed end grain on compression side
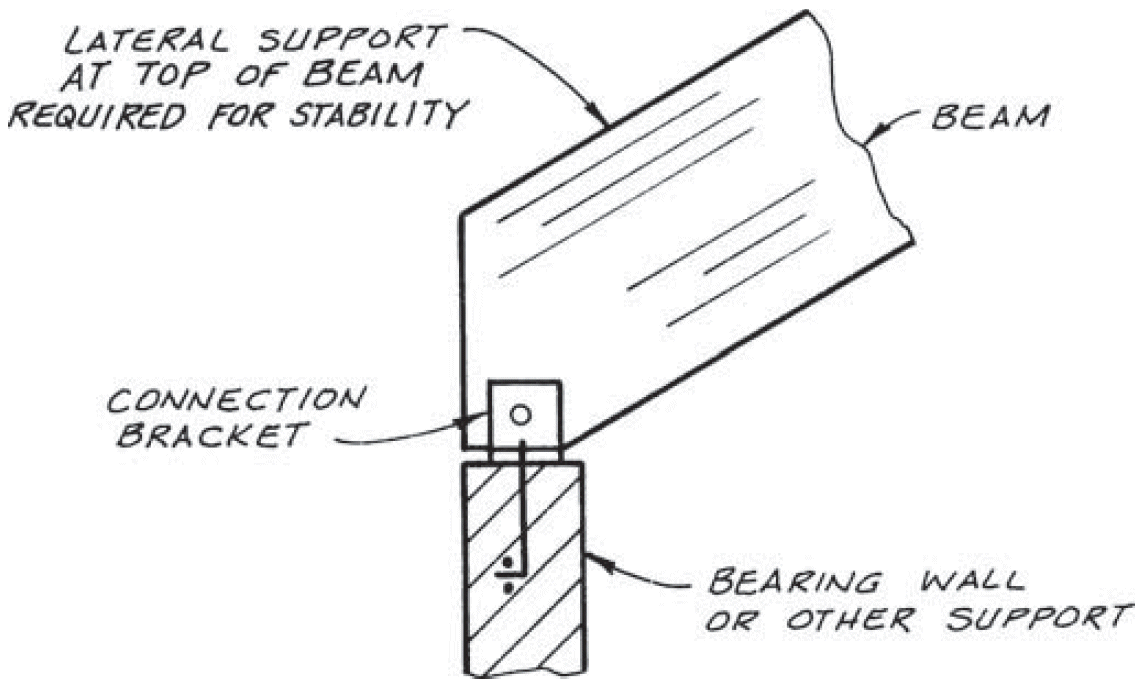
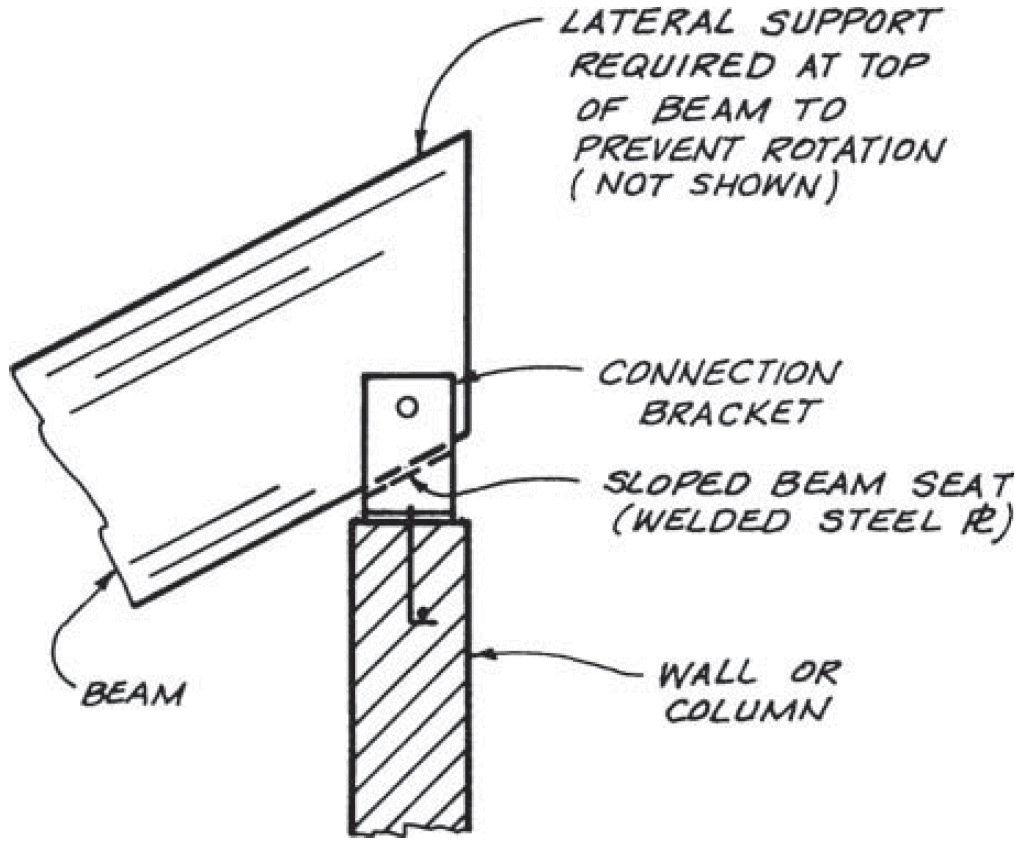
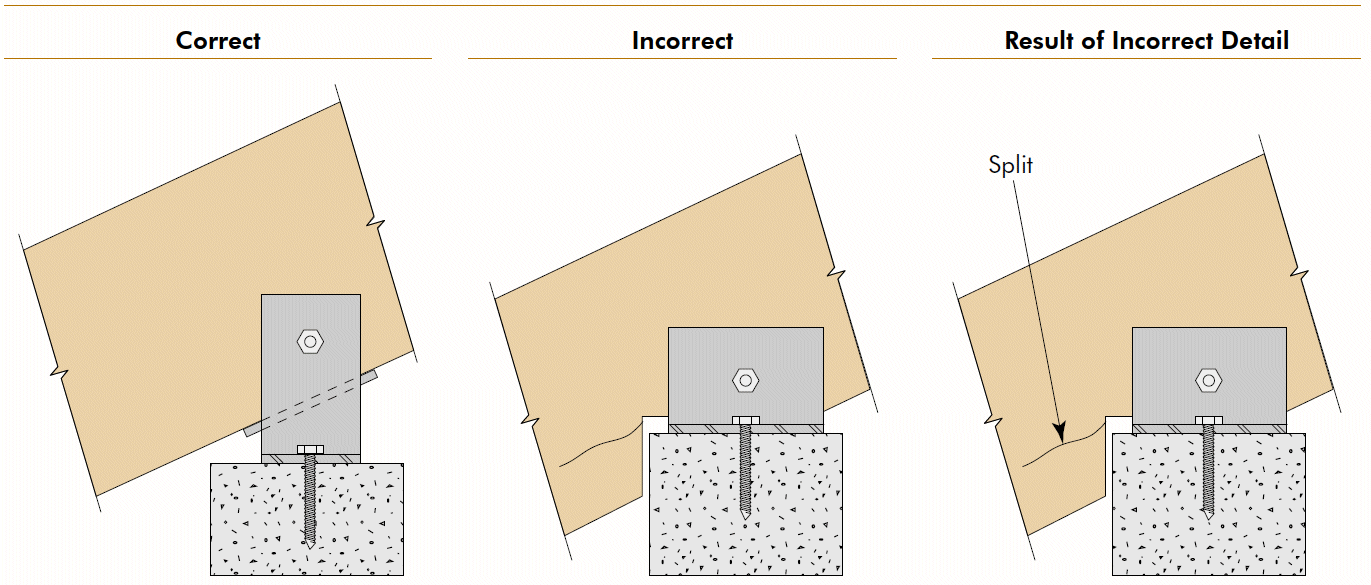
11. inclined beam - upper support
- problems
- shear strength
- stress concentration
- fix
- sloping seat, but be careful of eccentricity
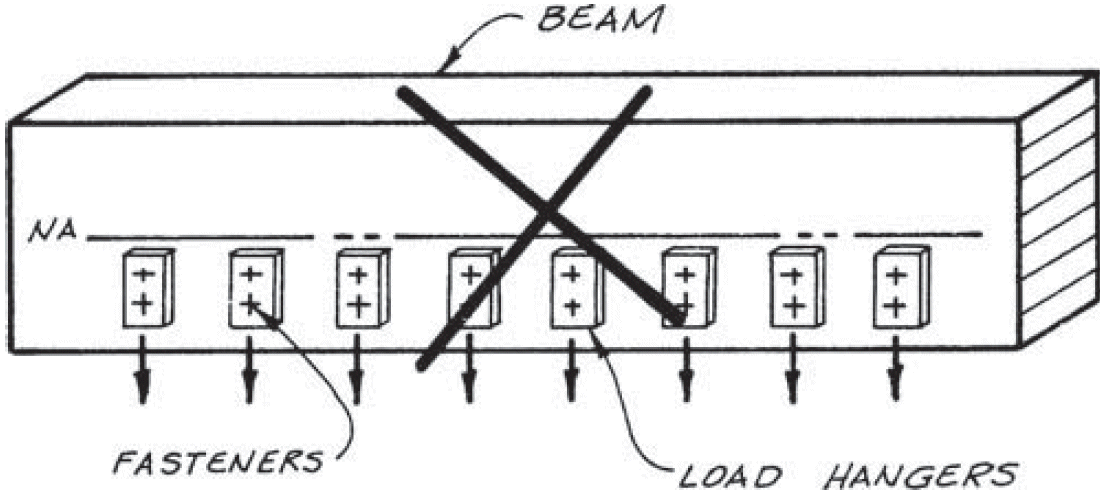
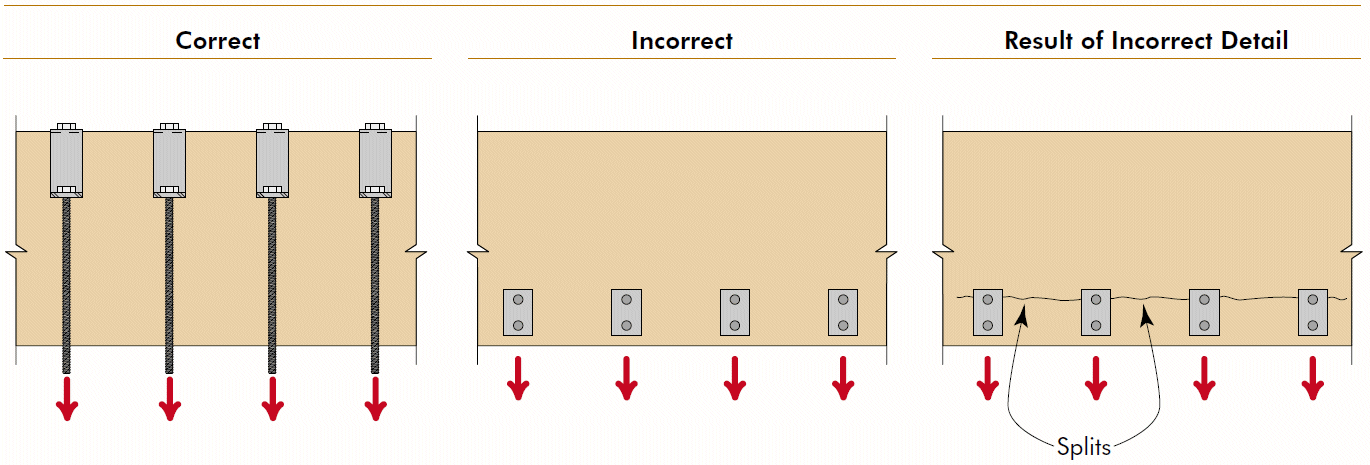
12. suspending multiple loads
- mechanical/electrical equipment OR joists framing into side of beam
- problems
- cross-grain tension
- horizontal shear
- stress concentrations
- fixes
- above neutral axis
- bearing on top
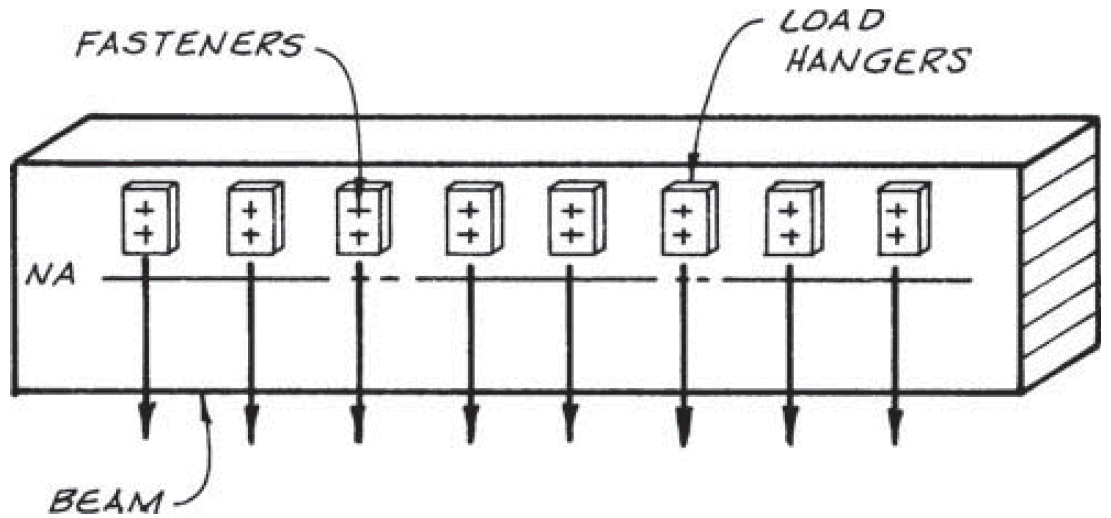
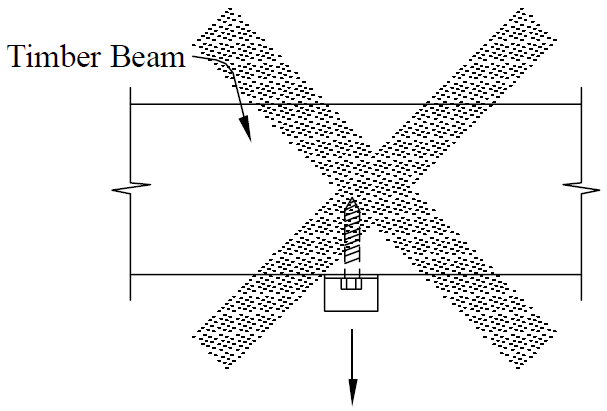
13. suspending isolated loads
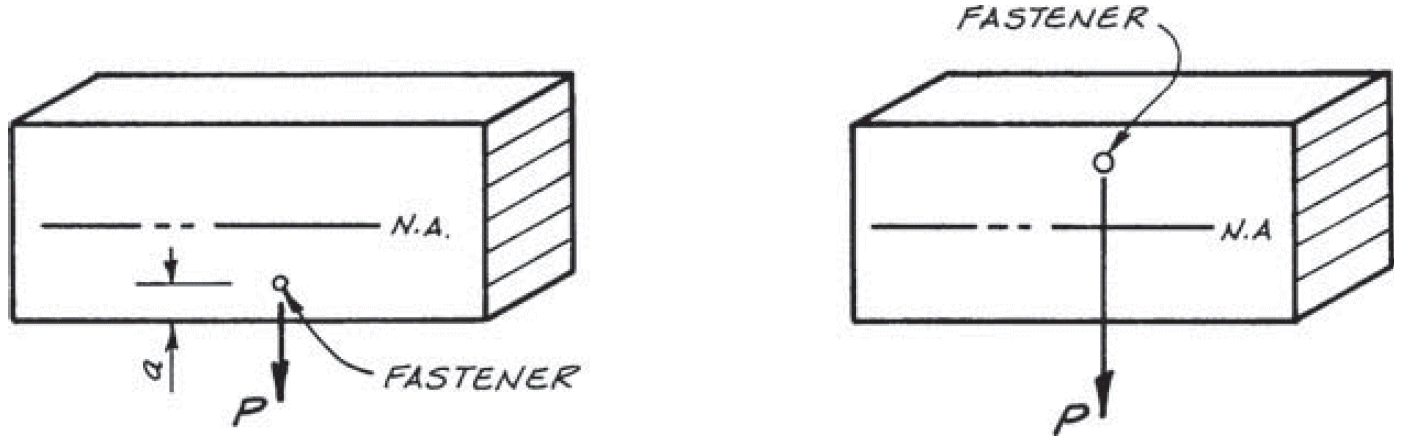
- problems
- similar to multiple loads
- fix
- limit to small loads + small fasteners
- minimum of 6 in. (AITC 104-2003)
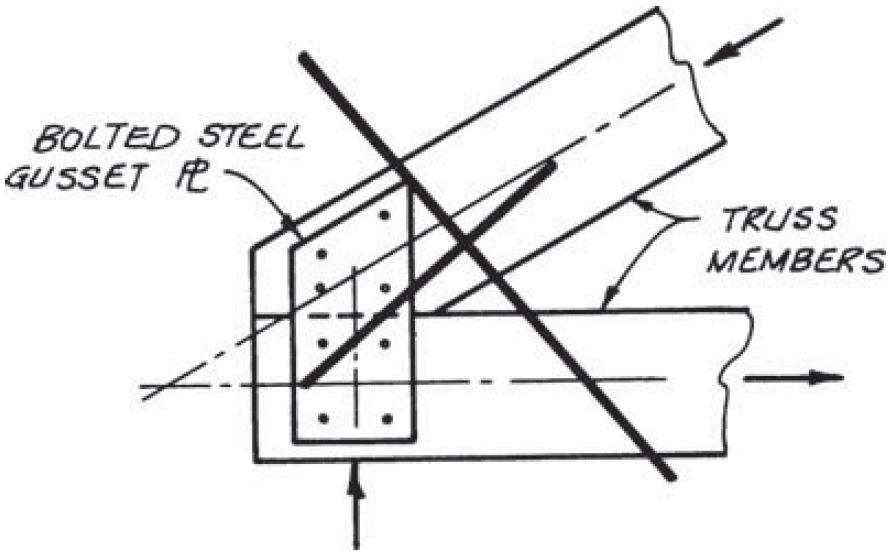
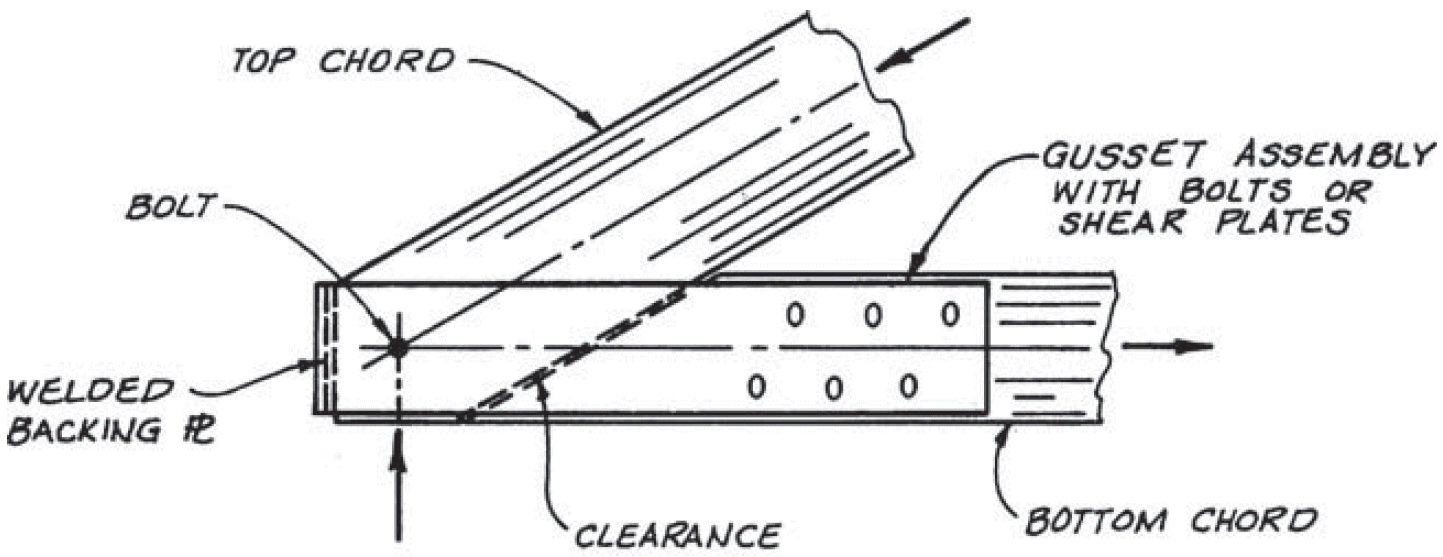
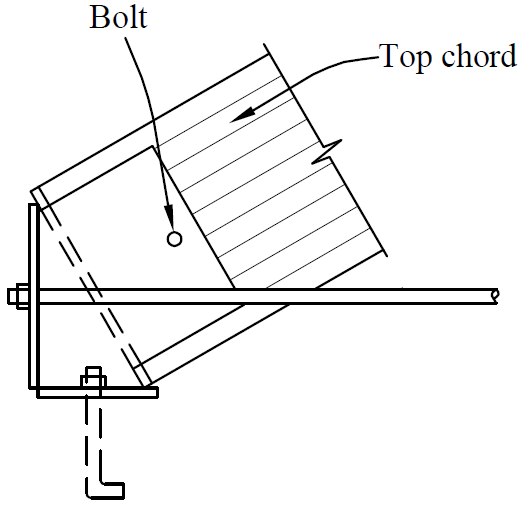
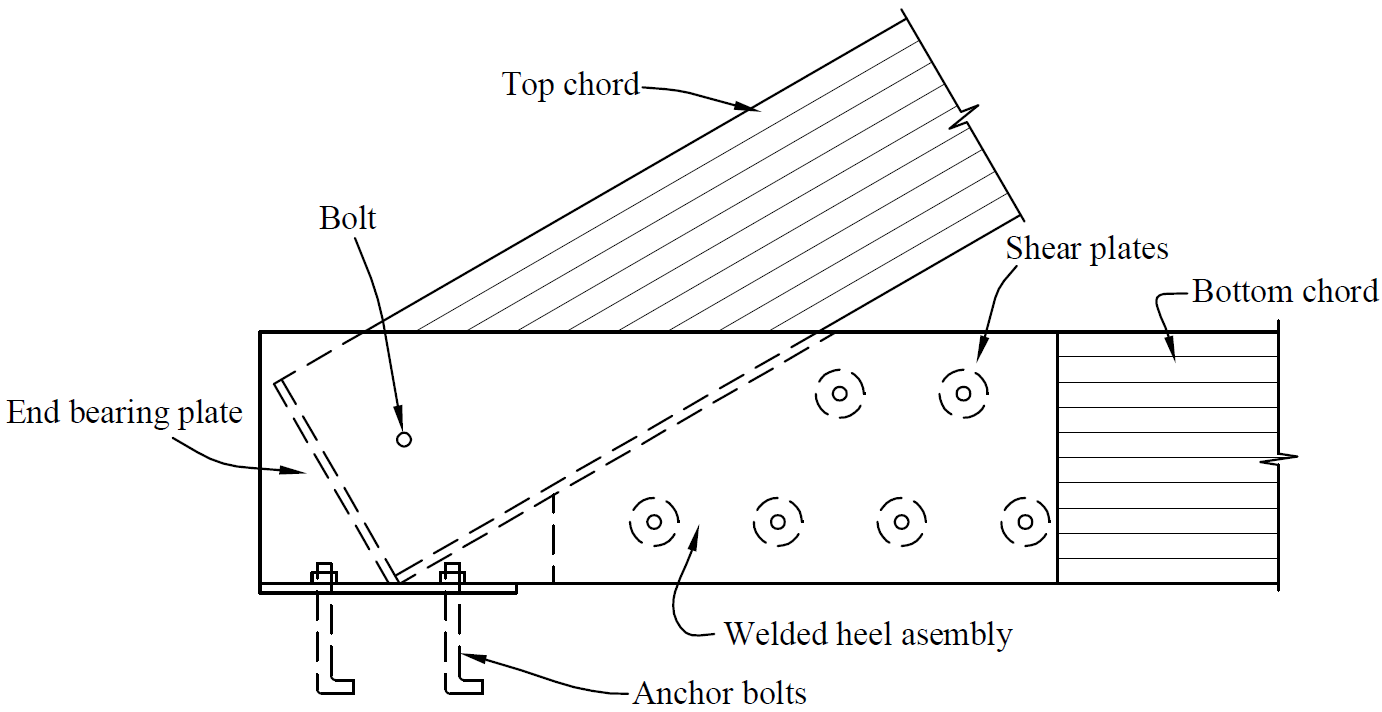
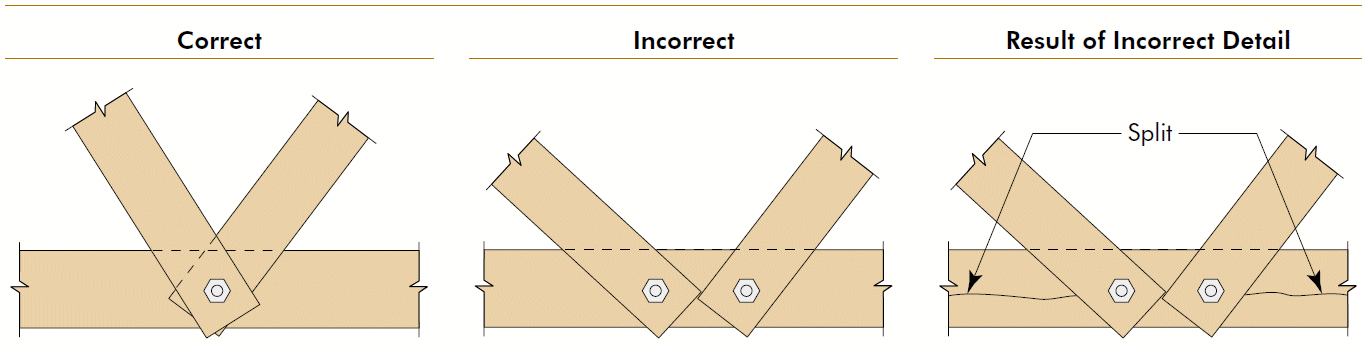
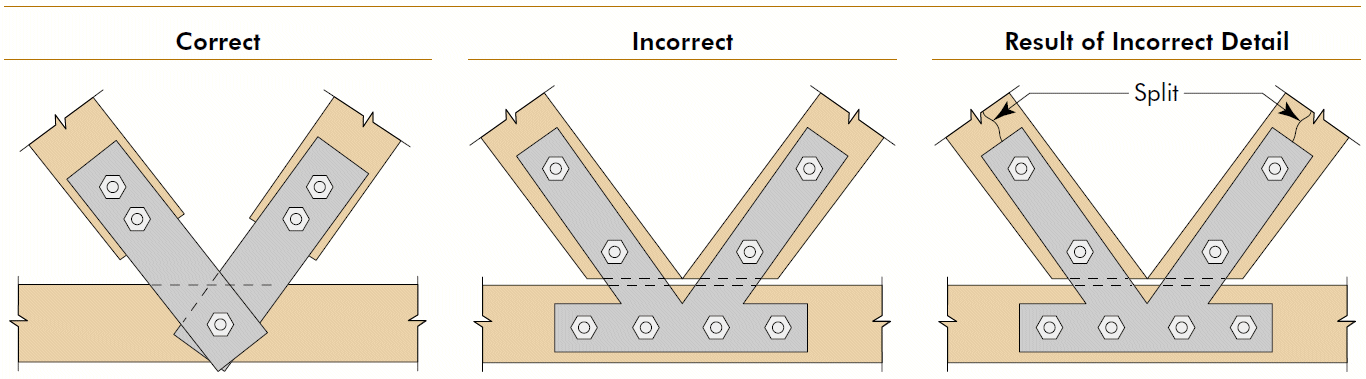
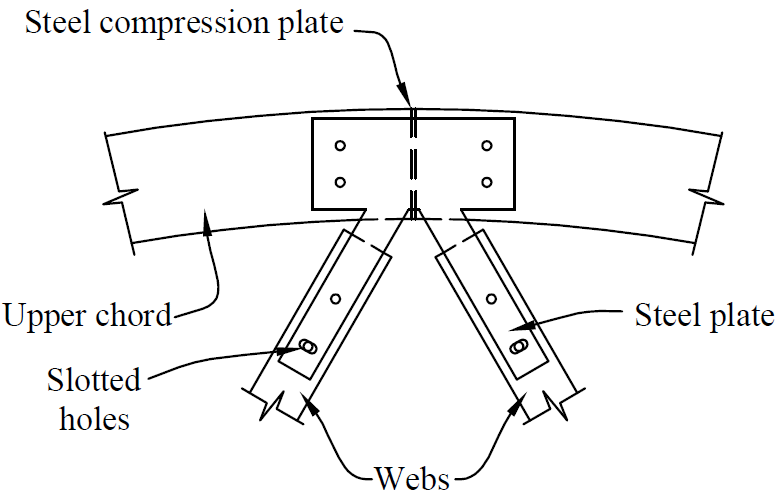
14. truss heel
- problems
- eccentricity (combined stresses)
- rotation
- fix
- bearing for top chord
- concentric forces
- rotation on single top-chord fastener
- slotted holes for shrinkage in bottom chord
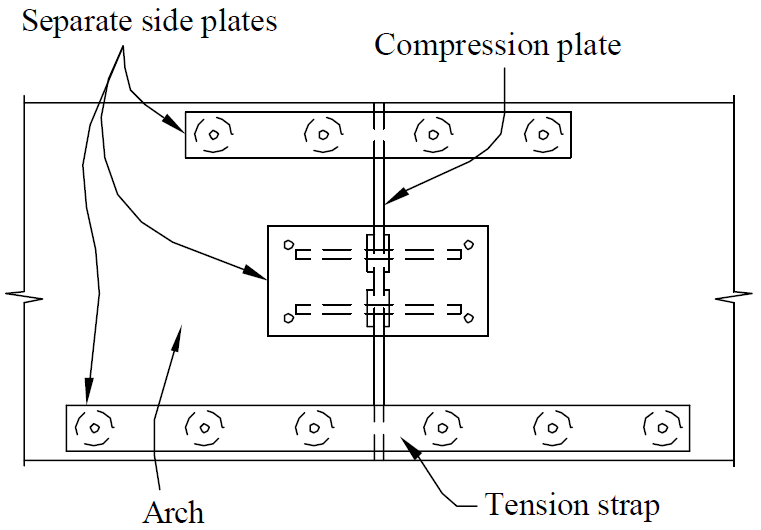
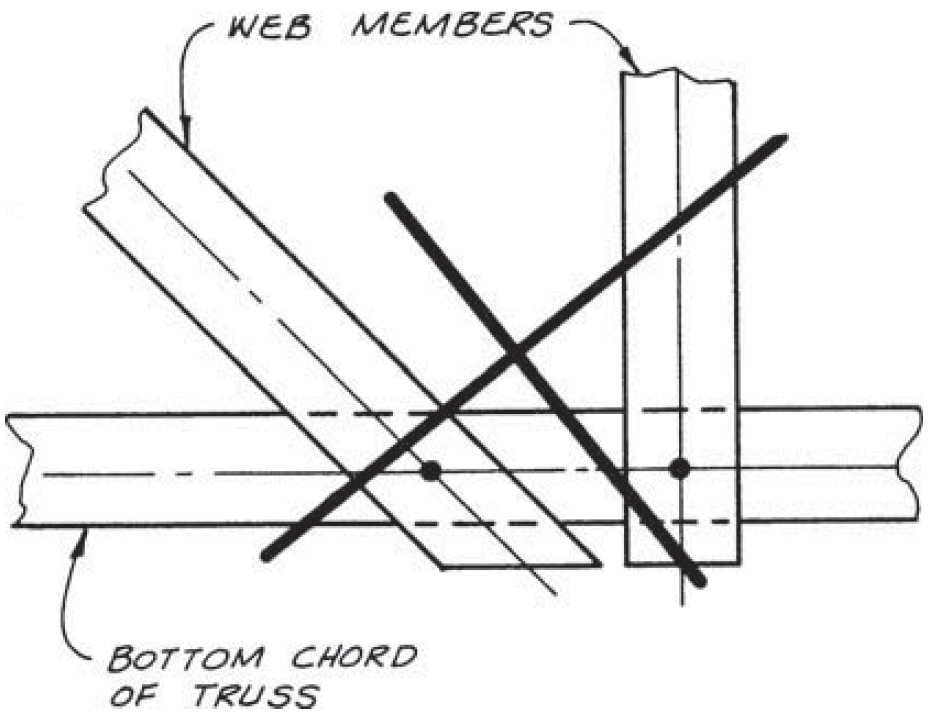
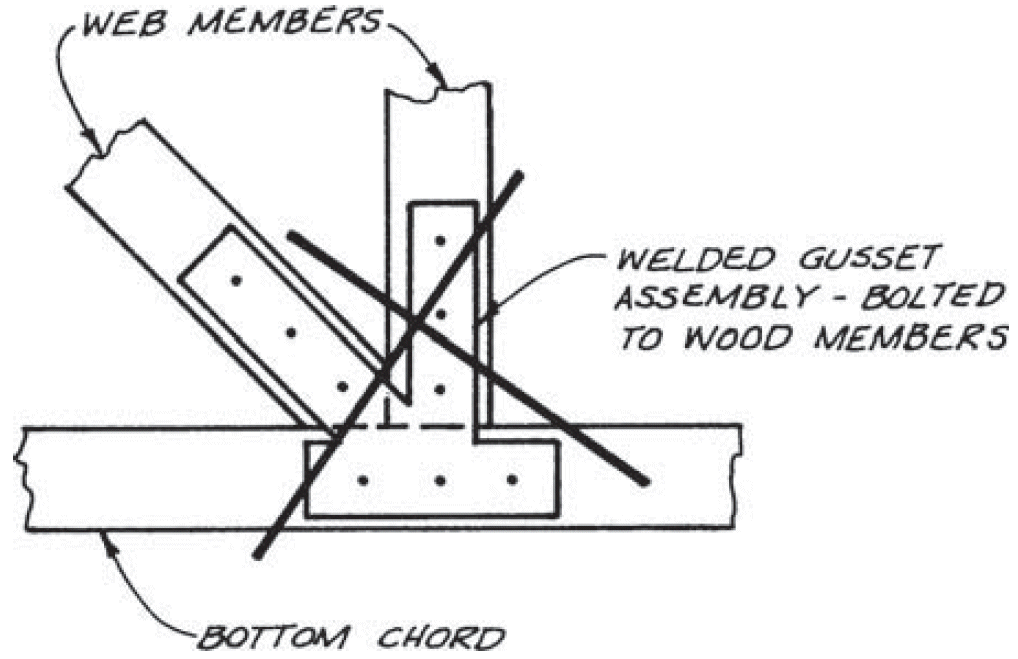
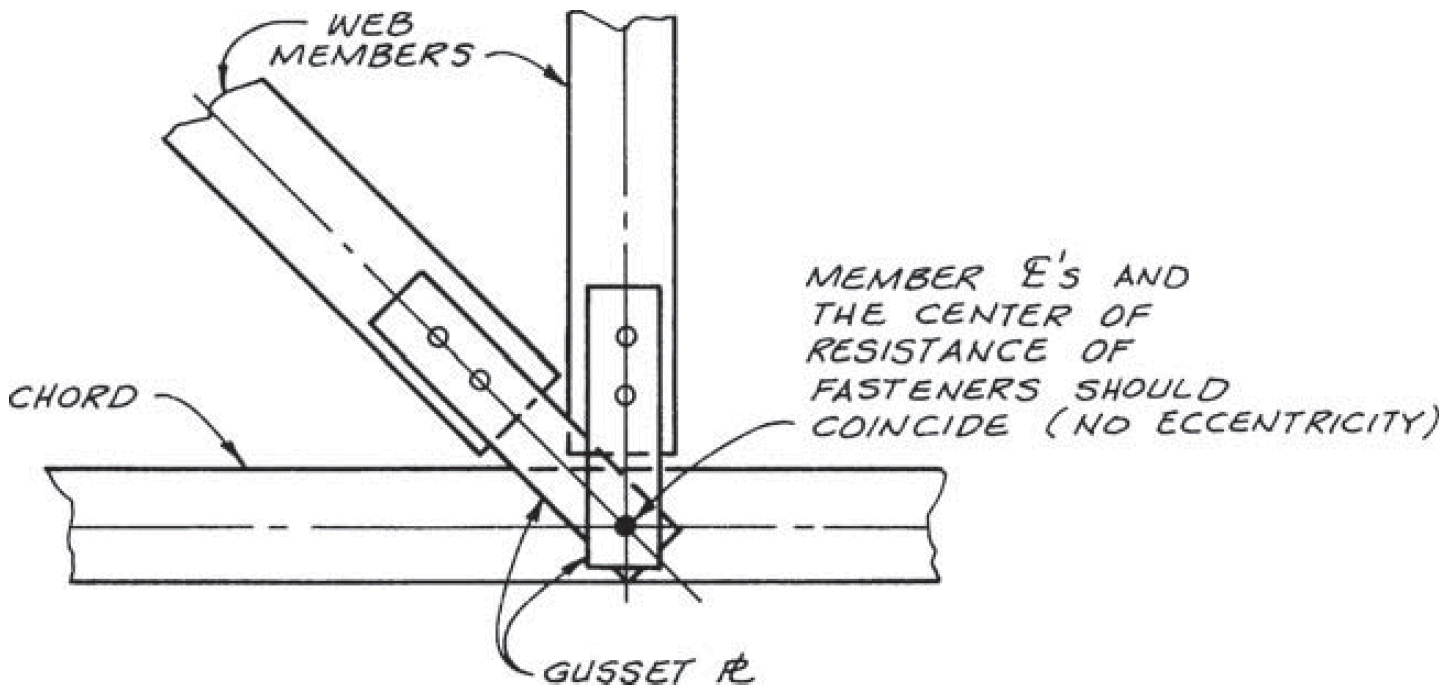
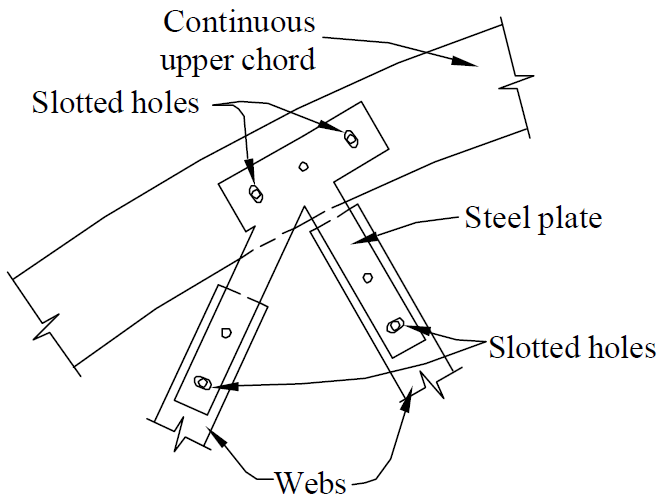
15. other truss joints
- example
- example
- problems
- eccentricity
- rigidity (limited deflection and rotation → prying and splitting)
- fixes
- separate gusset plates + shims
- slotted holes
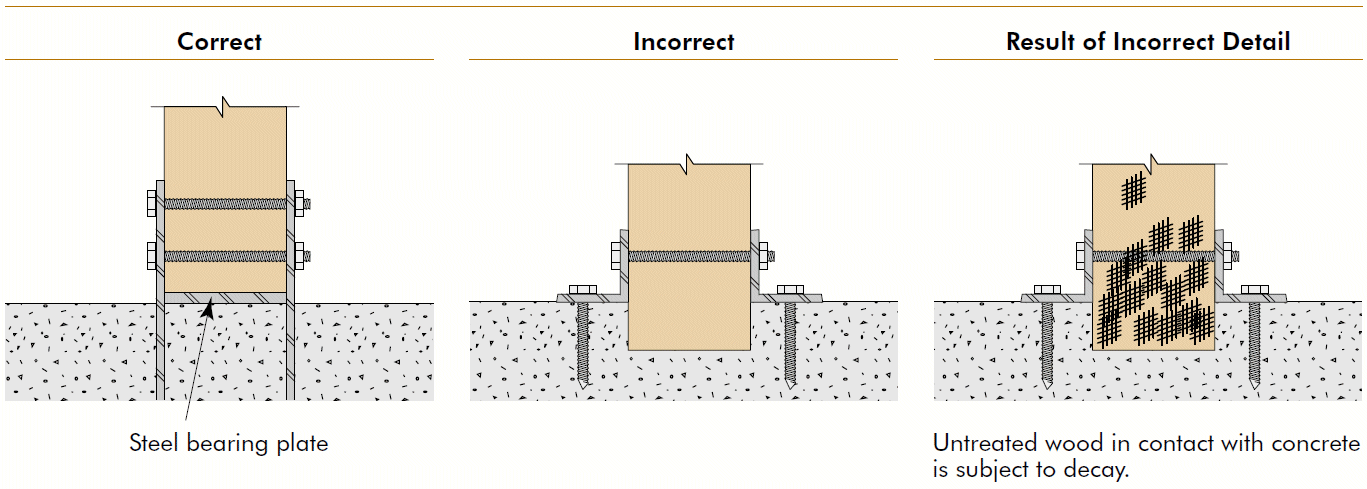
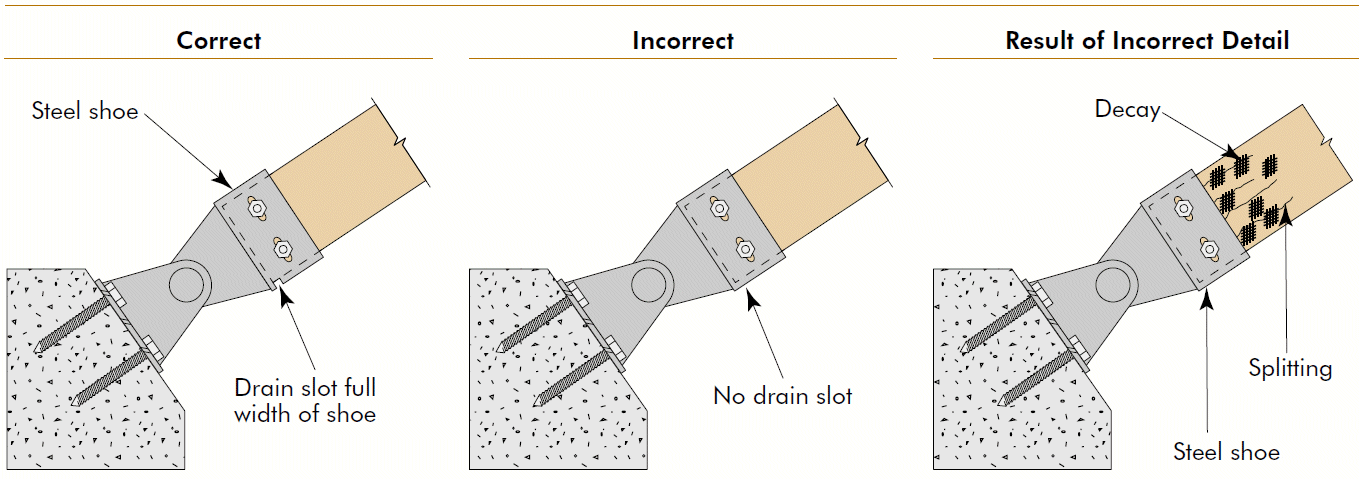
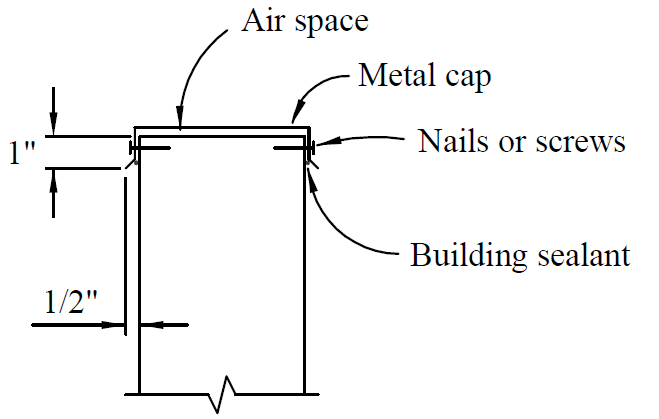
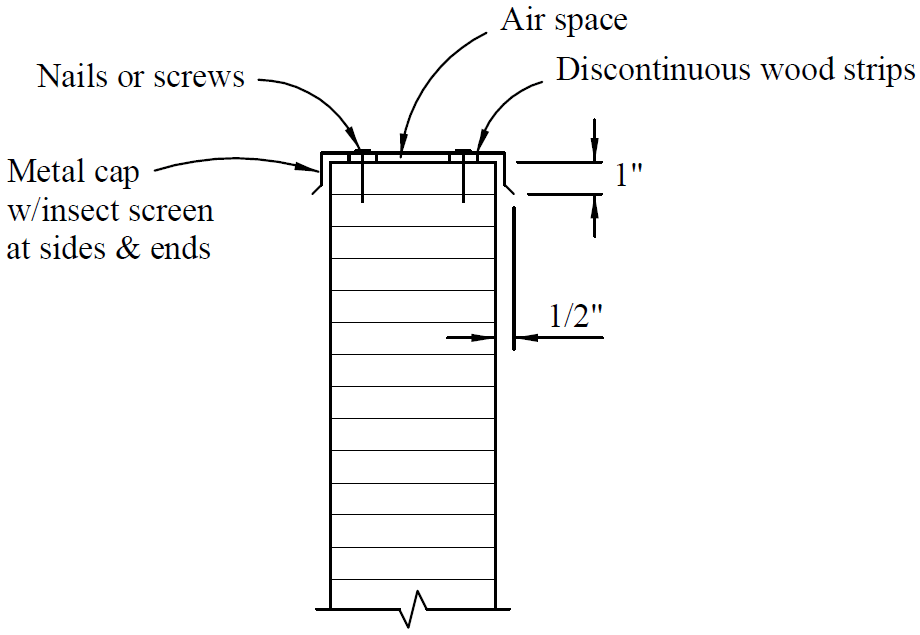
16. moisture protection
- problems
- wicking of moisture
- splashing
- inability to dry
- fixes
- treated wood
- barriers
- drain holes
- air gaps