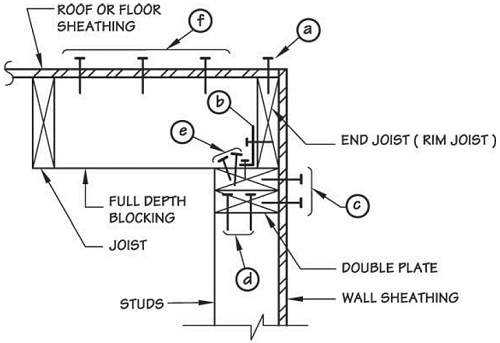
Load Flow in Transverse Wall Anchorage
|
forces // to wall (diaphragm shear)
- diaphragm sheathing → end/rim joist
- end/rim joist → top plate(s)
- framing anchor
- toenails (see
IBC section 2305.1.4)
- blocking
- top plate → wall sheathing
forces ⊥ to wall (wind or seismic)
- stud → top plate(s)
- top plate(s) → blocking to prevent rotation
- toenails (see
ASCE 7 section 12.11.2.2.3)
- framing anchor
- blocking → diaphragm sheathing
|
|
 |
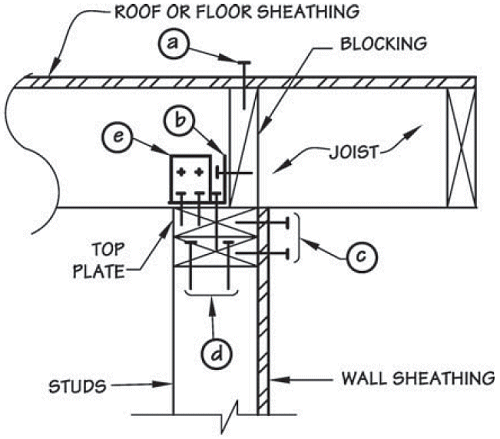
Load Flow in Longitudinal Wall Anchorage
|
forces // to wall (diaphragm shear)
- diaphragm sheathing → blocking
- blocking → top plate(s)
- framing anchor
- toenails (see
IBC section 2305.1.4)
- blocking
- top plate → wall sheathing
forces ⊥ to wall (wind or seismic)
- stud → top plate(s)
- top plate(s) → joist
- toenails (see
ASCE 7 section 12.11.2.2.3)
- framing anchor
- joist → diaphragm sheathing
|
|
 |