|
| |
Method of Shadow Profilometry:
 |
Consider a piece of corrugated cardboard, as an example. |
 |
If we cast a shadow using a remote light source and straightedge, we
create a shadow edge that follows the contours of the "rough" surface. The
shadow post is used to calculate the exact angle of the lighting. |
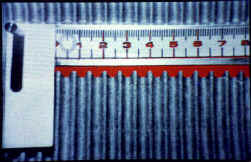 |
The image is digitized, and the shadow profile is identified. |
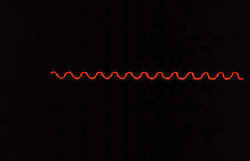 |
The edge of the shadow profile (roughness profile) is isolated. |
The above profile is analyzed for any of the traditional roughness parameters.
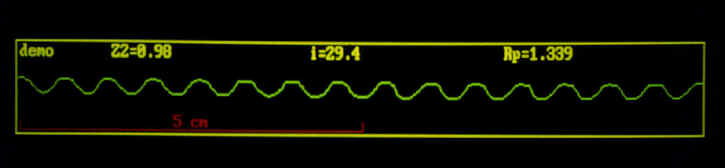
This techniques works on any rough or smooth surface.
REFERENCES:
Maerz, N. H., Franklin, J. A, and Bennett, C. A., 1990. Joint
roughness measurement using shadow profilometry. Int. J. of Rock Mech. Min. Sci. &
Geomech. Abst, v 27, pp. 329-343.
Maerz, N. H., and Franklin, J. A., 1990. Roughness scale
effect and fractal dimension. Proc. 1st Int. Workshop on Scale Effects in Rock Masses,
Loen, Norway, pp. 121-126.
|
|