Linear Impulse and Momentum of a Particle
Netwon's second law says that
![]()
where
.
When the forces are constants or functions of time only, we can separate variables and integrate with mass constant to get,
![]()
Rearranging,
![]()
where
| Initial linear momentum of the particle | |
| Linear impulse due to the forces acting on the particle during the time interval | |
| Final linear momentum of the particle |
Note that this is a vector equation, so we can also write it in component form.
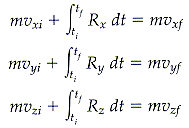
Also, it is sometimes useful to express the average impulse force as
![]()