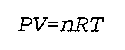
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the amount of gas
R is the Real Gas constant, with units appropriate for the units of pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas.
T is the temperature (in Kelvin because an absolute scale is necessary.)
Noggle- 3
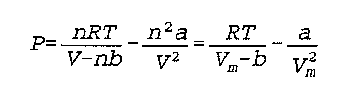
The constant a accounts for the attractive forces between gas molecules; PV=nRT assumed there were no attractions whatsoever.
The constant b accounts for the volume taken up by the gases; PV=nRT assumed gases to be points of infinitismally small volume.
V(m) is volume divided by amount in moles
Noggle- 5
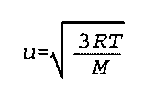
u is the root-mean-square speed
R is the Real Gas constant, with units appropriate for the units of pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas.
T is the temperature M is the molar mass
Noggle- 32
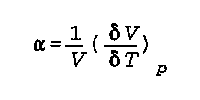
alpha is the coefficient of thermal expansion
V is the volume
delta V is the change in volume
delta T is the change in temperature P is the pressure and it is held constant
Noggle- 59
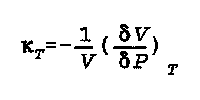
kappa(T) is the isothermal compressibility
V is the volume
delta V is the change in volume
delta P is the change in pressure
T is the temperature, and it is held constant.
Noggle- 71
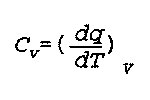
C(v) is the heat capacity at constant volume
q is the quantity of heat given off
T is the temperature
V is the volume
Noggle- 71
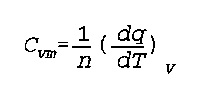
C(vm) is the molar heat capacity (constant volume)
n is moles
Noggle- 72
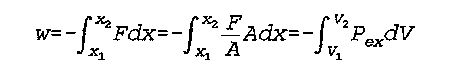
F is force
x is a one dimensional coordinate
A is area
V is volume
P(ex) is the pressure which opposes expansion
Noggle- 81
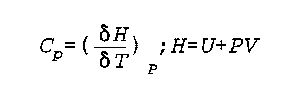
C(p) is Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
H is enthalpy
P is pressure
U is internal energy
V is volume
T is the temperature
Noggle- 86
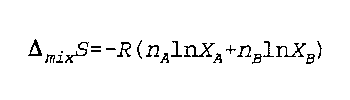
Delta (mix) S is the entropy of mixing for two gases
n is moles
R is the real gas constant
X is the mole fraction of the gas
Noggle- 136
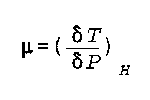
mu is the Joule Thompson coefficient
H is the enthalpy
P is the preaasure
T is the temperature
Noggle- 109
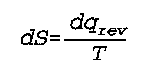
rev indicates the equation is valid only for a reversible process
q is the heat
S is the entropy
T is the temperature
Noggle- 128
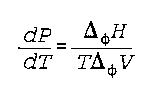
Delta phi X is the heat required at constant pressure and constant temperature, to effect a phase change
P is pressure
T is temperature
Delta phi V is the change in molar volume
Noggle- 175

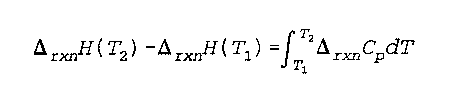
Delta (rxn) H(T) is the change in the enthalpy of a reaction at a specified temperature
Cp is the heat capacity at a constant pressure
T is the temperature
Noggle- 280
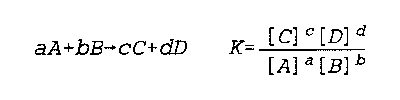
Small case variables (a,b,c,d) are stoichiometric coefficients
Large case variables (A,B,C,D) are chemical species
C and D are products, and A and B are reactants
K(a) is the thermodynamic equilibrium constant
Notice that what involves addition and subtraction in one equation relates to multiplication and division in the other
Noggle- 286
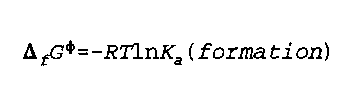
Delta(f)G phi is the standard free energy of formation
K(a) is the thermodynamic equilibrium constant
R is the Real Gas constant
T is temperature
Noggle- 291
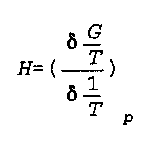
G is Free Energy
H is enthalpy
P is pressure
T is temperature
Noggle- 295
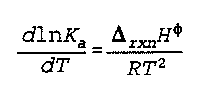
Delta(rxn)H(phi) is the change in enthalpy from the reaction
K(a) is thermodynamic equilibrium
T is temperature
Noggle- 298
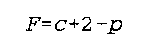
c is the number of components (I think this means c different 'types' of components--hey, components is a nebulous word, so I'll try to find an example of what it means
F is the degrees of freedom
p is the number of phases
Noggle- 339
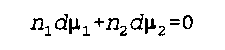
d mu is the change in chemical potential
n is the number of moles
Noggle- 356
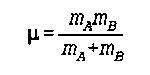
mu is the reduced mass
m is the mass of one of the two objects
Noggle- 1057
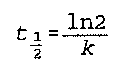
t is time
k is the "half life constant" (no specific name found)
Noggle- 521
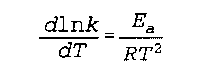
E(a) is the Arrhenius activation energy
k is the "rate constant" (no specific name found)
R is the Real Gas constant T is the temperature Noggle- 528
Arrhenius Activation Energy Equation
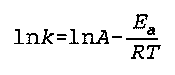
E(a) is the Arrhenius activation energy
k is the "rate constant" (no specific name found)
R is the Real Gas constant
T is the temperature
Noggle- 528
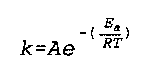
E(a) is the Arrhenius activation energy
k is the "rate constant" (no specific name found)
R is the Real Gas constant
T is the temperature
Noggle- 529
PChem29.gif is now available for a new equation
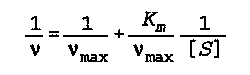
v is the velocity of the overall (biochemical) reaction
v(max) is the maximum velocity the reaction could achieve
K(m) is the Michaelis constant
[S] is the substrate concentration
Noggle- 582
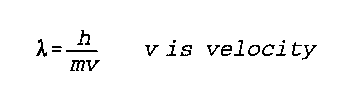
Lambda is wavelength of the object
h is Planck's constant
m is the mass of the object
v is the velocity of the object
Noggle- 614
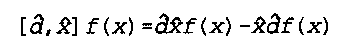
x and d are operators, as signified by the "carrot" symbol
f(x) is a generic function
[d,x] represents the commutator of variables d and x
Noggle- 618