Chem 2/5 Labs FS2001
Colligative Properties Post-Laboratory Questions
Section/TA________________
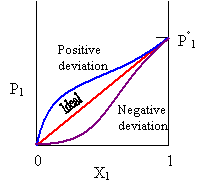
P1 = X1 P°1.
In the ideal case, this leads to a linear plot of the vapor pressure of the solvent, P1, versus the mole fraction of solvent, X1. However nonideal solutions deviate from linearity either negatively or positively as shown below:
LaCl3 (s) --> La3+ (aq) + 3 Cl- (aq)
Suppose 0.2453 grams of LaCl3 is dissolved in 100.0 grams of H2O. What is the boiling point of the solution at atmospheric pressure?