Heat Transfer Probes for gas-solid, gas-liquid, and gas-liquid-solid systems
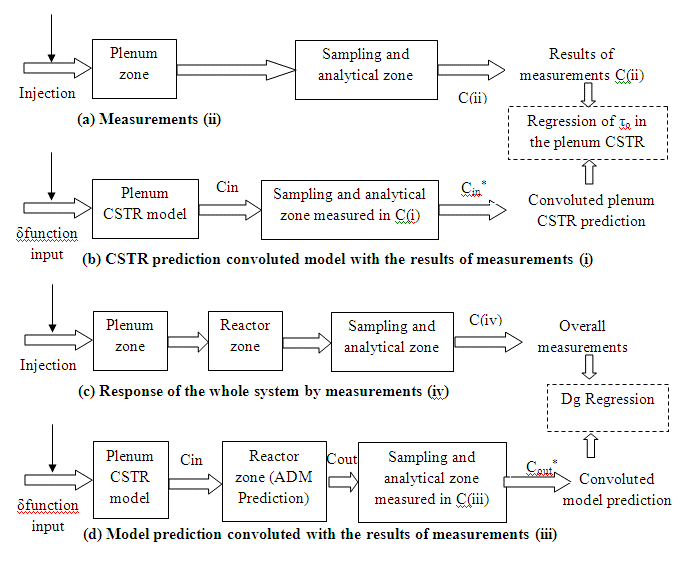
Heat transfer is a novel technique of fast-response time used to obtain precise measurements of local instantaneous heat transfer coefficient and rates through a bulk in multiphase flow systems. It has been designed to measure both the local heat flux from the heat transfer probe to the bulk and the surface temperature of the probe simultaneously with the response time of the sensor being about 0.02 s. This technique provided an accurate, quantitative and reliable detailed data under computer monitoring.
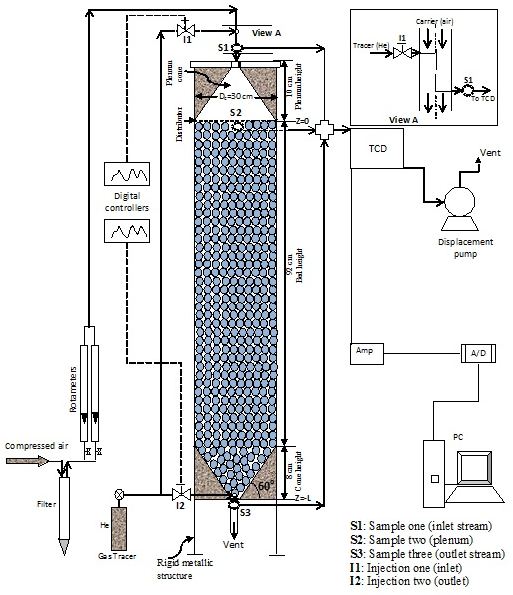
It has been developed in order to cover a wide range of the experimental work requirements and operating conditions (–185 °C to 260°C).The components of the developed heat transfer technique are: constant heat flux probe, DC power supply, amplifier, thermocouple sensors, data acquisition (DAQ) system and P. They are of two types, rod-type and spherical-type.
The principal gradient method of heat transfer working is based on the measuring the temperature differences between two known thermal resistances of the layered gases. The methodology, algorithms and programs have been developed and implemented in order to convert the local instantaneous heat transfer coefficient between the constant heat flux probe and the surrounding gas phase dispersion into local time-averaged heat transfer coefficient for whole system.