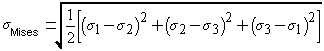what is it?
mechanics - the study of forces and their effects
source: EM Program at UIUCrigid body mechanics (Classical mechanics)
deformable body mechanics (Mechanics of materials)
- Statics - the study of bodies in equilibrium (zero acceleration)
- Dynamics - the study of the accelerated motion of bodies
fluid mechanics
- determine the stresses, strains, and displacements in structures due to various loadings
- understand the mechanical behavior of structures (up to the loads that cause failure)
solving mechanics problems
problem format and homework suggestions
- simply going through the motions
- rarely analyzes engineering problems clearly and precisely
- emerging engineering skills
- clear, precise, and well-reasoned, though with occasional lapses into weak reasoning
- often analyzes engineering problems clearly and precisely, formulates information accurately, distinguishes the relevant from the irrelevant, and recognizes key questionable assumptions
statics
A rigid body is a collection of particles that remain at fixed distances from each other at all times and under all conditions of loading.
The rigid-body concept represents an idealization of the true situation, since all real bodies will change shape to a certain extent when they are subjected to a system of forces. When it is assumed that the body is rigid (free of deformation), the material properties of the body are not required for the analysis of forces and their effects on the body.
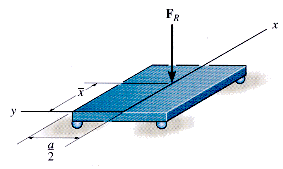
free-body diagram - drawing of an object and the external forces acting on it
- Select the object to be isolated.
- Redraw the object isolated from its surroundings. Show relevant dimensions and angles.
- Draw all external forces acting on the object, including gravity.
- Choose a coordinate system.
force - the action of one body on another ... spatial energy potential?
Concentrated Force
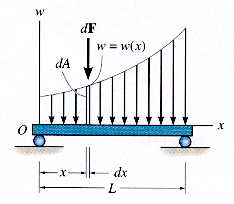
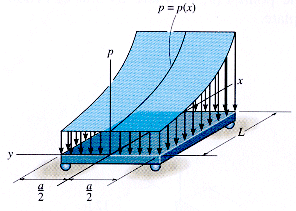
Force Distributed
Over a LineForce Distributed
Over an Area
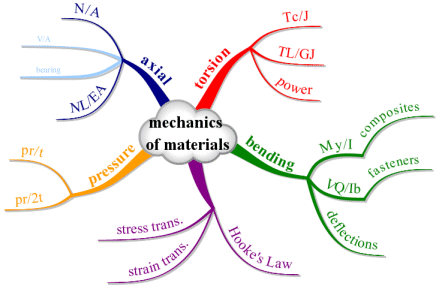
mechanics of materials
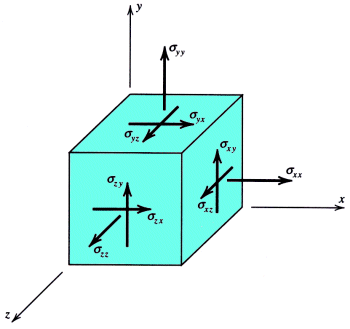
stress has pressure units (psi or Pa)
stresses typically cannot be added and subtracted like scalars
pressurex beam flexure
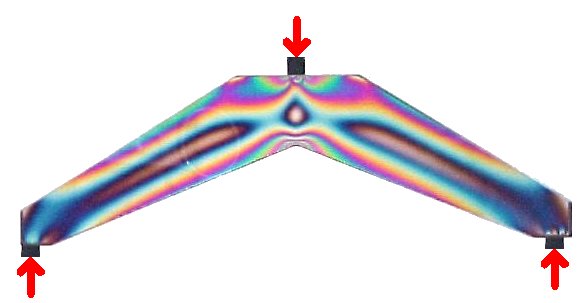
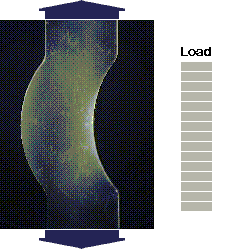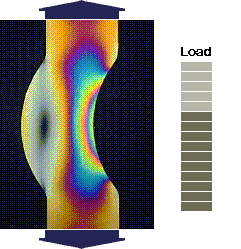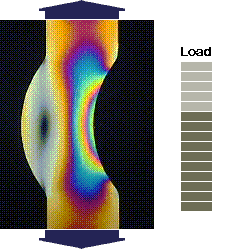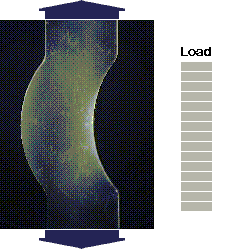
source: Jeff Thomas, April 2000
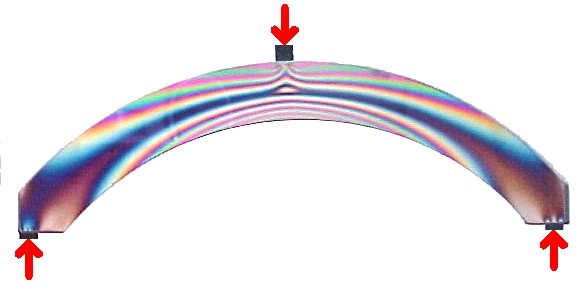
source: Measurements Group Inc.the MoM formulas have many limitations...
Length
Metals Bone Muscle Wood 0.000000000000001 m sub-atomic sub-atomic sub-atomic sub-atomic 0.000000000001 m atomic,
crystallographic,
monomeric0.000000001 m collagen molecule tropo-collagen,
micro-fibrilmicrostructure protofibrils hydroxyapatite,
collagen fibrilfibril sub-fibril microfibrils,
cellulose fibers,
laminated cell walls0.000001 m collagen fiber lamellae fibroblasts cell diameter Haversian osteon fascicle 0.001 m macrostructure cell length organ organ growth rings 1 m organ system organ system trunk ...but serve as a good starting point for understanding how force is transmitted through an object