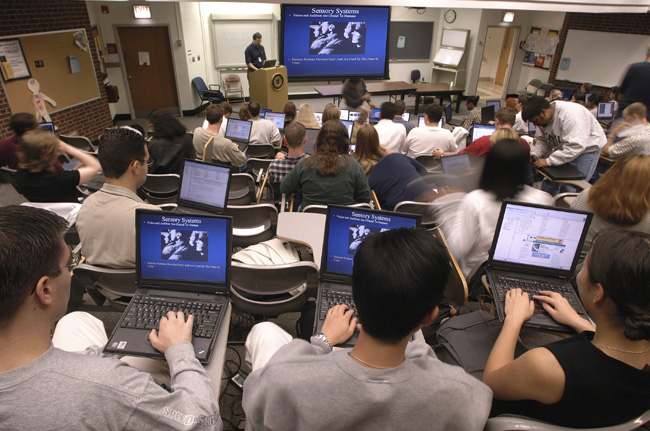
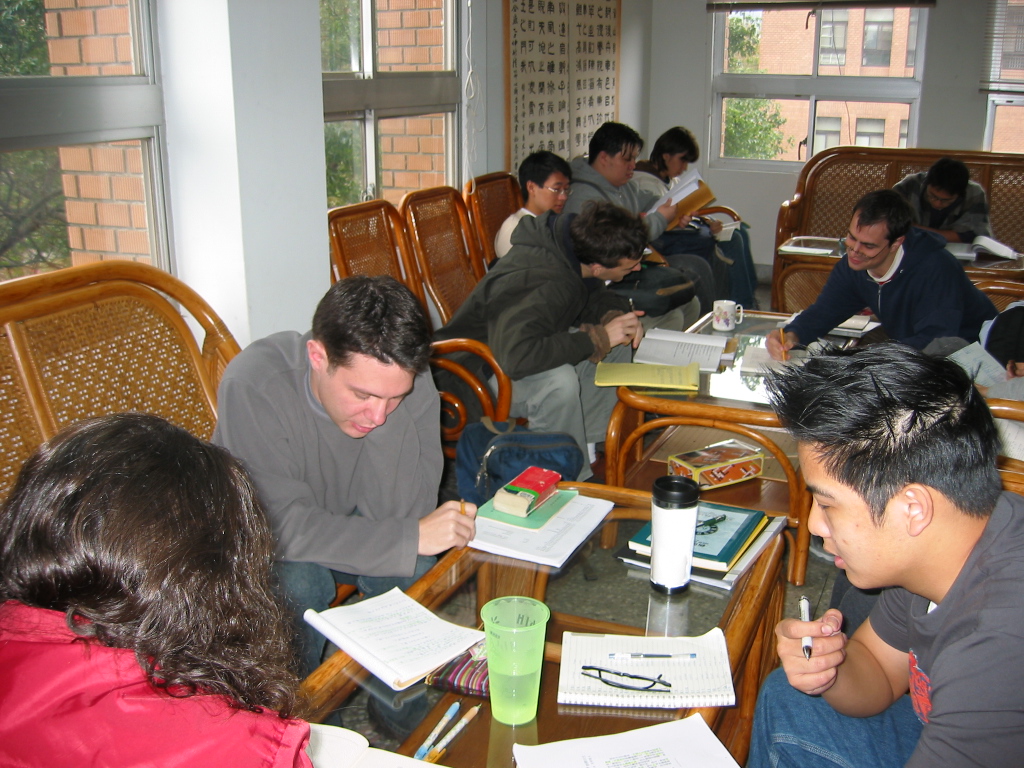
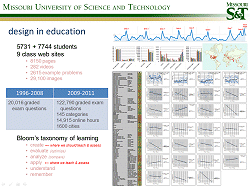
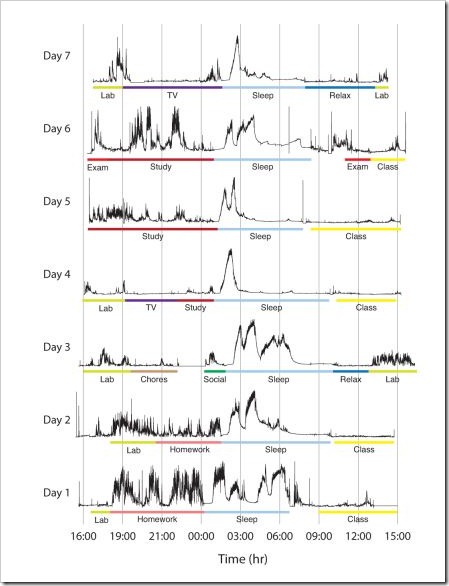
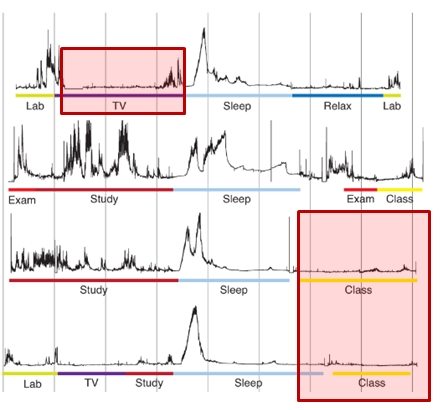
What makes for a comfortable pillow?
source
source
Pressure in liquids and gases
Stress in solids
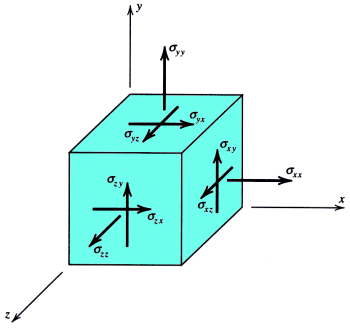
Augustin Louis Cauchy [kō-shē, 1789-1857]…applies the notion of pressure on a plane (a concept which was familiar to him from hydrodynamics) and assumes that this pressure is no longer normal to the plane upon which it acts in an elastic body. … The total stress on an infinitesimal element of a plane taken within a deformed elastic body is defined as the resultant of all the actions of the molecules situated on one side of the plane upon the molecules on the other, the directions of which (actions) intersect the element under consideration. By dividing the total force by the area of the element, the magnitude of stress is obtained. -- Timoshenko, S. P. (1983), History of strength of materials. McGraw-Hill.
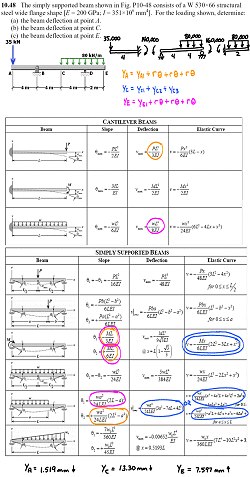
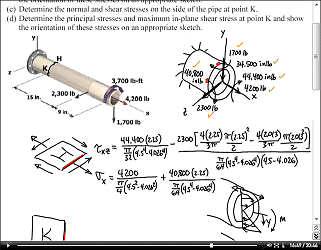
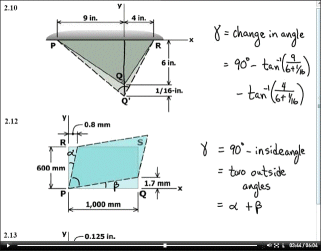
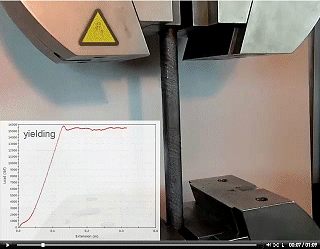
Chapters 1-3 cover stress, strain and how they are related.
Statics vs Mechanics of Materials
tractor-trailer axle by David Krier on March 31, 2009
Typical
22% get D, F, WD
Statics
1X 52% 2X 30% 3X+ 17%
Mechanics of Materials
1X 61% 2X 32% 3X+ 7%
Freshman 0 Sophomore 1 Junior 50 Senior 65 Grad 0
Aerospace Engineering 5 Architectural Engineering 3 Ceramic Engineering 6 Civil Engineering 9 Computer/Electrical Engineering 0 Engineering Management 20 Environmental Engineering 6 Geological Engineering 2 Mechanical Engineering 39 Metallurgical Engineering 11 Nuclear Engineering 5 Petroleum Engineering 15 Undeclared 2
Teaching Aids
436 problem solutions
309 problem strategies
Videos
Type of Video Number of Videos Average Video
Lengthproblem-solution 140 8.4 min. problem-strategy 6 16.7 min. concept 49 5.4 min. demonstration 28 1.9 min. experiment 5 2.0 min. Total 228 28 hours
problem solutions problem strategies concepts demonstrations experiments
What is Learning?
There are essential minimal conditions for cultivating educated minds.
All of the traditional content areas of schools may be, but typically are not, taught so as to conduce to those standards, abilities, traits.
. B6 - create B5 - optimize B4 - compare B3 - calculate - 100% of incoming S&T freshman have trouble with Apply skill (they are not taught in K-12) B2 - paraphrase - 60% of incoming S&T freshman have trouble with Understand skill B1 - read - 20% of incoming S&T freshman have trouble with Remember skill
Everyone must cultivate the skills and dispositions of the critical mind within their minds, using their own thinking.
One person can influence another, finally, only with the cooperation of that other.
And from the inside of your own mind, your own thinking usually appears to be damned good, and not really in need of change.
Semester Bloom Level 1
Questions
- remember -Bloom Level 2
Questions
- understand -Bloom Level 3
Questions
- calculate -Bloom Level 4
Questions
- compare -fall 2012 90% 75% 74% 64% spring 2013 93% 79% 76% 62%
Multiple-Choice Exams: An Obstacle for Higher-Level Thinking in Introductory Science Classes, by Kathrin F. Stanger-Hall, CBE—Life Sciences, Education Vol. 11, 294–306, Fall 2012
Cognitively passive learning behaviors
- I previewed the reading before class.
- I came to class.
- I read the assigned text.
- I reviewed my class notes.
- I rewrote my notes.
- I made index cards.
- I highlighted the text.
- I looked up information.
- I asked a classmate or tutor to explain the material to me.
Cognitively active learning behaviors
- I asked myself: “How does it work?” and “Why does it work this way?”
- I drew my own flowcharts or diagrams.
- I broke down complex processes step-by-step.
- I wrote my own study questions.
- I reorganized the class information.
- I compared and contrasted.
- I fit all the facts into a bigger picture.
- I tried to figure out the answer before looking it up.
- I closed my notes and tested how much I remembered.
- I asked myself: “How are individual steps connected?” and “Why are they connected?”
- I drew and labeled diagrams from memory and figured out missing pieces.
- I asked myself: “How does this impact my life?” and “What does it tell me about my body?”
- I used Bloom’s taxonomy to write my own study questions
What makes for a good learning environment?
A Wearable Sensor for Unobtrusive, Long-Term Assessment of Electrodermal Activity (pdf)
Making Homework More Effective (slides 18 & 21)
Understanding Students of This Generation
1912-1921 Depression Era (birth years shown)
1922-1927 World War II Generation
1928-1945 Post-War Cohort, The Lucky Few
1946-1954 Boomers I, Baby Boomers
1955-1965 Boomers II, Generation Jones
1966-1976 Generation X, Baby Bust
1977-1994 Generation Y, Echo Boomers, Millenniums, Net or Me-First Generation
1995-2012 Generation Z, Generation Next, We Generation
props:
sheet for people to fill out if they add the class (name, SN,
section, reference number for each section), blank add &
section change slips, markers, tape measure, boards: 1.25"x48" poplar
dowel rod, (2) 1"x3"x48" #2 pine, (3)
1"x2"x48" #2 pine (there wasn't enough
time to break things in Summer 2010)
props: chalk, gloves, aluminum bars of various shapes, sheet for people to fill out if they add the class (name, SN, section, reference number for each section), blank add & section change slips, solutions notebook, markers, statics quizzes, tape measure, boards: 1.25"x48" poplar dowel rod, (2) 1"x3"x48" #2 pine, (3) 1"x2"x48" #2 pine