Hardware-Software Co-Design in an Undergraduate Microcontroller Laboratory
Hardware-software
co-design is an essential skill for fast and efficient development of products
in high-tech computer industries. Our laboratories and software tools
help introduce these skills at the undergraduate level. Using a
simulation model of the 8051 microcontroller, the laboratories take students through
the 4 fundamental steps of hardware-software co-design:
|
Students design and connect peripherals for the 8051 microcontroller. Students may simulate hardware (without software) at this stage. |
|
|
Students develop software for the 8051 microcontroller to be used with hardware they have already developed. Students may simulate software (without hardware) at his stage. |
|
|
Using the 8051 simulation model, students fully test their designs by simulating hardware and software together. Through co-simulation, errors may be found and removed quickly, before final implementation. |
|
|
|
The student's hardware-software design is implemented on the Xess XS40 board. Students test their design by observing logic levels at pin probe points or by observing operation of external components, such as the on-board LED display, parallel port, vga display, or other attached peripherals. |
As part of these laboratories,
we have also developed a simplified version of the 8051 microcontroller, called
the WIMP51, and an animated visual interface to the WIMP to help teach concepts
of processor architecture and of co-design of hardware-software systems at the
chip-level.
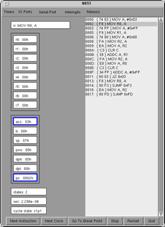
We have also developed
a hardware-software debugging interface that allows a user to view the values
of registers and memory inside the 8051 while co-simulating their hardware and
software design instruction-by-instruction or clock-by-clock. The interface works on top of Mentor Graphics
ModelSim to perform the actual simulation.
8051 Hardware-Software Debugger
These laboratories
teach students fundamental concepts of hardware-software co-design.
There are several publications on
these materials. Some good overviews
include:
·
D. Beetner and H. Pottinger, “Laboratories Introducing Embedded Systems,
Hardware-Software Co-Design, and Computer Organization,” 38th ASEE
·
L. Verma, H. J.
Pottinger, and D. G. Beetner, "A Software Debugger Interface for an 8051
Hardware Model," 2003 Conference on
Microelectronic Systems Education, June 2003.